Page 45 - Energize April 2021
P. 45
TECHNICAL
Tubular steel poles (monopoles) galloping criteria, rolling clearances, and structural geometry.
One of the most significant advances in compact OHL design The technology used leverages physics to maximise electrical
has been the use of tubular steel poles to replace lattice masts. performance. The phase separation is reduced into a compact “delta”
Monopoles consist of interlocking sections of continuous, uniform configuration (Figure 10) and the conductor diameter, number of
tapered design, having a polygonal cross section (i.e., 8-sided, subconductors, and bundle spacing are optimised. Figure 11 shows
12-sided, and 16-sided), with longitudinal welding. Monopoles the insulator assembly for one 345 kV circuit for a 3-conductor bundle.
consist of two or more sections with telescopic joints to achieve the
required height.
The volume of the structure is reduced significantly from that
of traditional latticed towers. Monopoles require a smaller base
foundation (footprint) and are easier to transport and install than
lattice structures. They can be manufactured in any configuration
required and the polygonal shape provides flat surfaces that facilitate
the mounting of insulators and other items.
The round shape of the monopole fits in with the natural
surroundings. Nature rarely presents angular elements in design,
except for the mineral world. Trees, grasses, mountains, and plains
have principally smooth rounded forms and appeal to natural senses.
The monopole could be combined with other curved elements such
as pole arms to provide a natural looking installation.
Compact transmission line examples
The breakthrough overhead line design (BOLD) compact
transmission system 8
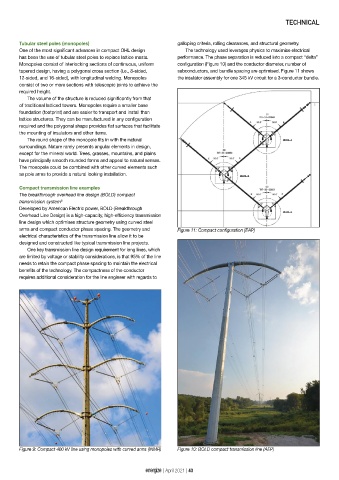
Developed by American Electric power, BOLD (Breakthrough
Overhead Line Design) is a high‐capacity, high‐efficiency transmission
line design which optimises structure geometry using curved steel
arms and compact conductor phase spacing. The geometry and Figure 11: Compact configuration [EAP]
electrical characteristics of the transmission line allow it to be
designed and constructed like typical transmission line projects.
One key transmission line design requirement for long lines, which
are limited by voltage or stability considerations, is that 95% of the line
needs to retain the compact phase spacing to maintain the electrical
benefits of the technology. The compactness of the conductor
requires additional consideration for the line engineer with regards to
Figure 9: Compact 400 kV line using monopoles with curved arms (INMR) Figure 10: BOLD compact transmission line (AEP)
energize | April 2021 | 43