Page 44 - Energize April 2021
P. 44
TECHNICAL
provide to the assembly vertical, transverse, and longitudinal loads Among the key benefits of composite cross-arms is that insulator-
capability. These assemblies are generally used to longitudinally swing under windy conditions is eliminated by the metal clamping
stabilize long sequences of horizontal vees. They can also be used assemblies. There is also no requirement for additional tower height to
to replace parts of steel cross-arms on existing towers for voltage accommodate the length of the insulator string itself. Using composite
upgrades and compaction of the route. insulating cross-arms can effectively raise heights of conductors by
the length of the insulator string, i.e., about 4 m in the case of a 400
kV line. The use of insulated cross arms with lattice towers can:
5
• Resolve ground clearance problems on existing lines.
• Allow greater sag on existing or new conductors, critical to
improving power transfer capacity, since it enables conductors
to run at highest rated temperatures while still not infringing
ground clearances.
• Facilitate voltage upgrading due to improved clearances from
towers, especially since risk of blow out is mitigated.
• Permit more compact towers on new routes with smaller
foundations and therefore reduced costs.
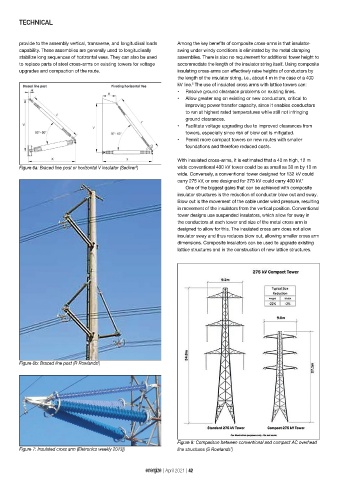
With insulated cross-arms, it is estimated that a 40 m high, 12 m
Figure 6a: Braced line post or horizontal V insulator (Sediver ) 6 wide conventional 400 kV tower could be as small as 30 m by 10 m
wide. Conversely, a conventional tower designed for 132 kV could
carry 275 kV, or one designed for 275 kV could carry 400 kV. 7
One of the biggest gains that can be achieved with composite
insulator structures is the reduction of conductor blow out and sway.
Blow out is the movement of the cable under wind pressure, resulting
in movement of the insulators from the vertical position. Conventional
tower designs use suspended insulators, which allow for sway in
the conductors at each tower and size of the metal cross arm is
designed to allow for this. The insulated cross arm does not allow
insulator sway and thus reduces blow out, allowing smaller cross arm
dimensions. Composite insulators can be used to upgrade existing
lattice structures and in the construction of new lattice structures.
Figure 6b: Braced line post (R Rowlands ) 3
Figure 8: Comparison between conventional and compact AC overhead
Figure 7: Insulated cross arm (Eletronics weekly 2013]) line structures (S Rowlands ) 7
energize | April 2021 | 42