Page 62 - Energize July 2022
P. 62
TECHNICAL
The free piston engine typically consists of the following
components:
• Combustion chamber or cylinder: The combustion cylinder is a
rigid cylindrical chamber where the combustion of the air-fuel
mixture takes place, and the housing inside of which piston moves.
• Piston: The rigid cylindrical part of the engine which produces
reciprocating motion inside the combustion chamber due to the
combustion of the air-fuel mixture.
• Spark plug or fuel injector: The spark plug is used to ignite the
air-fuel mixture and fuel injector injects the fuel during the
compression stroke during compression ignition which results in
combustion.
• Bounce cylinder: This is a cylinder with a piston which is connected
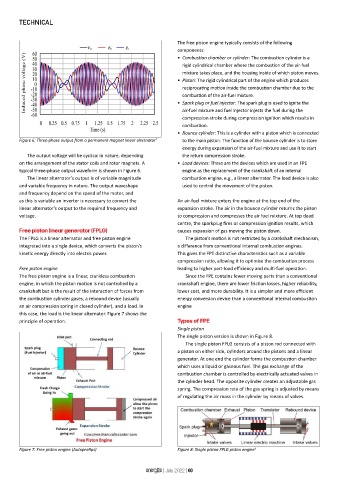
Figure 6: Three-phase output from a permanent magnet linear alternator 7 to the main piston. The function of the bounce cylinder is to store
energy during expansion of the air-fuel mixture and use it to start
The output voltage will be cyclical in nature, depending the return compression stroke.
on the arrangement of the stator coils and rotor magnets. A • Load devices: These are the devices which are used in an FPE
typical three-phase output waveform is shown in Figure 6. engine as the replacement of the crankshaft of an internal
The linear alternator’s output is of variable magnitude combustion engine, e.g., a linear alternator. The load device is also
and variable frequency in nature. The output waveshape used to control the movement of the piston.
and frequency depend on the speed of the motor, and
as this is variable an inverter is necessary to convert the An air-fuel mixture enters the engine at the top end of the
linear alternator’s output to the required frequency and expansion stroke. The air in the bounce cylinder returns the piston
voltage. to compression and compresses the air fuel mixture. At top dead
centre, the sparkplug fires or compression ignition results, which
Free piston linear generator (FPLG) causes expansion of gas moving the piston down.
The FPLG is a linear alternator and free piston engine The piston’s motion is not restricted by a crankshaft mechanism,
integrated into a single device, which converts the piston’s a difference from conventional internal combustion engines.
kinetic energy directly into electric power. This gives the FPE distinctive characteristics such as a variable
compression ratio, allowing it to optimise the combustion process
Free piston engine leading to higher part-load efficiency and multi-fuel operation.
The free piston engine is a linear, crankless combustion Since the FPE contains fewer moving parts than a conventional
engine, in which the piston motion is not controlled by a crankshaft engine, there are lower friction losses, higher reliability,
crankshaft but is the result of the interaction of forces from lower cost, and more durability. It is a simpler and more efficient
the combustion cylinder gases, a rebound device (usually energy conversion device than a conventional internal combustion
an air compression spring in closed cylinder), and a load. In engine
this case, the load is the linear alternator. Figure 7 shows the
principle of operation. Types of FPE
Single piston
The single piston version is shown in Figure 8.
The single piston FPLG consists of a piston rod connected with
a piston on either side, cylinders around the pistons and a linear
generator. At one end the cylinder forms the combustion chamber
which uses a liquid or gaseous fuel. The gas exchange of the
combustion chamber is controlled by electrically actuated valves in
the cylinder head. The opposite cylinder creates an adjustable gas
spring. The compression rate of the gas spring is adjusted by means
of regulating the air mass in the cylinder by means of valves.
Figure 7: Free piston engine (Autoprotips) Figure 8: Single piston FPLG piston engine 4
energize | July 2022 | 60