Page 66 - Energize July 2022
P. 66
TECHNICAL
inrush current for a longer time than a lightly loaded motor, as can
be seen in Figure 3. Similarly, if the supply voltage is low, the motor
starting time will be extended along with the duration of the inrush
current, as is shown in Figure 4. This makes it more likely that
protective devices will trip.
When characterising motor inrush current, a waveform capture
of at least several seconds is required so that the current can
be observed from inrush through to steady state. In addition, a
single inrush test may not provide enough information to resolve
problems. Motors often start and stop multiple times throughout
the day, with varying loads and changing supply voltages affecting
the inrush current. Monitoring should, therefore, be carried
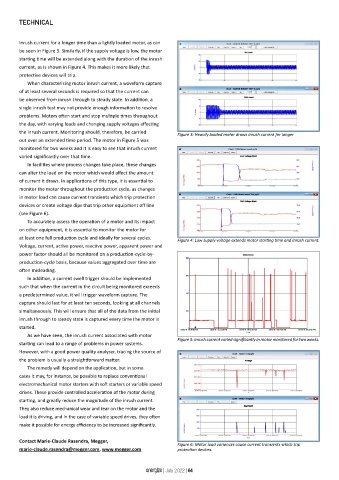
Figure 3: Heavily loaded motor draws inrush current for longer
out over an extended time period. The motor in Figure 5 was
monitored for two weeks and it is easy to see that inrush current
varied significantly over that time.
In facilities where process changes take place, these changes
can alter the load on the motor which would affect the amount
of current it draws. In applications of this type, it is essential to
monitor the motor throughout the production cycle, as changes
in motor load can cause current transients which trip protection
devices or create voltage dips that trip other equipment off line
(see Figure 6).
To accurately assess the operation of a motor and its impact
on other equipment, it is essential to monitor the motor for
at least one full production cycle and ideally for several cycles. Figure 4: Low supply voltage extends motor starting time and inrush current.
Voltage, current, active power, reactive power, apparent power and
power factor should all be monitored on a production-cycle-by-
production-cycle basis, because values aggregated over time are
often misleading.
In addition, a current swell trigger should be implemented
such that when the current in the circuit being monitored exceeds
a predetermined value, it will trigger waveform capture. The
capture should last for at least ten seconds, looking at all channels
simultaneously. This will ensure that all of the data from the initial
inrush through to steady state is captured every time the motor is
started.
As we have seen, the inrush current associated with motor
Figure 5: Inrush current varied significantly in motor monitored for two weeks.
starting can lead to a range of problems in power systems.
However, with a good power quality analyser, tracing the source of
the problem is usually a straightforward matter.
The remedy will depend on the application, but in some
cases it may, for instance, be possible to replace conventional
electromechanical motor starters with soft starters or variable speed
drives. These provide controlled acceleration of the motor during
starting, and greatly reduce the magnitude of the inrush current.
They also reduce mechanical wear and tear on the motor and the
load it is driving, and in the case of variable speed drives, they often
make it possible for energy efficiency to be increased significantly.
Contact Marie-Claude Rasendra, Megger, Figure 6: Motor load variances cause current transients which trip
marie-claude.rasendra@megger.com, www.megger.com protection devices.
energize | July 2022 | 64