Page 70 - Energize July 2022
P. 70
TECHNICAL
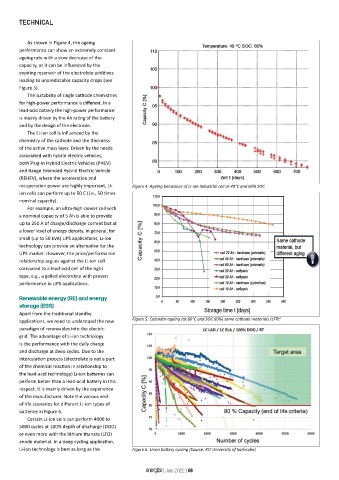
As shown in Figure 4, the ageing
performance can show an extremely constant
ageing rate with a slow decrease of the
capacity, or it can be influenced by the
expiring reservoir of the electrolyte additives
leading to unpredictable capacity drops (see
Figure 5).
The suitability of single cathode chemistries
for high-power performance is different. In a
lead-acid battery the high-power performance
is mainly driven by the Ah rating of the battery
and by the design of the electrode.
The Li-ion cell is influenced by the
chemistry of the cathode and the thickness
of the active mass layer. Driven by the needs
associated with hybrid electric vehicles,
both Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
and Range Extended Hybrid Electric Vehicle
(REHEV), where the acceleration and
recuperation power are highly important, Li- Figure 4: Ageing behaviour of Li-ion industrial cell at 40°C and 60% SOC
ion cells can perform up to 50 C (i.e., 50 times
nominal capacity).
For example, an ultra-high-power cell with
a nominal capacity of 5 Ah is able to provide
up to 250 A of charge/discharge current but at
a lower level of energy density. In general, for
small (up to 50 kVA) UPS applications, Li-ion
technology can provide an alternative for the
UPS market. However, the price/performance
relationship argues against the Li-ion cell
compared to a lead-acid cell of the right
type, e.g., a gelled electrolyte with proven
performance in UPS applications.
Renewable energy (RE) and energy
storage (ESS)
Apart from the traditional standby
applications, we need to understand the new Figure 5: Calendar ageing (at 60°C and SOC 60%) same cathode materials (LFP) 2
paradigm of renewables into the electric
grid. The advantage of Li-ion technology
is the performance with the daily charge
and discharge at deep cycles. Due to the
intercalation process (electrolyte is not a part
of the chemical reaction in relationship to
the lead-acid technology) Li-ion batteries can
perform better than a lead-acid battery in this
respect. It is mainly driven by the experience
of the manufacturer. Note the various end-
of-life scenarios for different Li-ion types of
batteries in Figure 6.
Certain Li-ion cells can perform 4000 to
5000 cycles at 100% depth of discharge (DOD)
or even more with the lithium titanate (LTO)
anode material. In a deep cycling application,
Li-ion technology is best as long as the Figure 6: Li-ion battery cycling (Source: KIT University of Karlsruhe)
energize | July 2022 | 68