Page 75 - Energize July 2022
P. 75
TECHNICAL
Types of fuel cell and a silicon carbide structure which holds the phosphoric acid
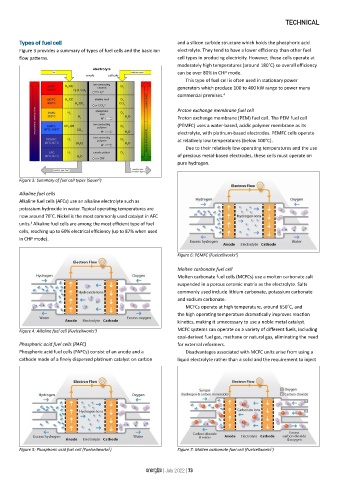
Figure 3 provides a summary of types of fuel cells and the basic ion electrolyte. They tend to have a lower efficiency than other fuel
flow patterns. cell types in producing electricity. However, these cells operate at
moderately high temperatures (around 180˚C) so overall efficiency
can be over 80% in CHP mode.
This type of fuel cell is often used in stationary power
generators which produce 100 to 400 kW range to power many
commercial premises. 4
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell. The PEM fuel cell
(PEMFC) uses a water-based, acidic polymer membrane as its
electrolyte, with platinum-based electrodes. PEMFC cells operate
at relatively low temperatures (below 100°C).
Due to their relatively low operating temperatures and the use
of precious metal-based electrodes, these cells must operate on
pure hydrogen.
Figure 3: Summary of fuel cell types (Sauer )
2
Alkaline fuel cells
Alkaline fuel cells (AFCs) use an alkaline electrolyte such as
potassium hydroxide in water. Typical operating temperatures are
now around 70˚C. Nickel is the most commonly used catalyst in AFC
units. Alkaline fuel cells are among the most efficient type of fuel
3
cells, reaching up to 60% electrical efficiency (up to 87% when used
in CHP mode).
Figure 6: PEMFC (Fuelcellworks )
3
Molten carbonate fuel cell
Molten carbonate fuel cells (MCFCs) use a molten carbonate salt
suspended in a porous ceramic matrix as the electrolyte. Salts
commonly used include lithium carbonate, potassium carbonate
and sodium carbonate.
MCFCs operate at high temperature, around 650˚C, and
the high operating temperature dramatically improves reaction
kinetics, making it unnecessary to use a noble metal catalyst.
Figure 4: Alkaline fuel cell (Fuelcellworks ) 3 MCFC systems can operate on a variety of different fuels, including
coal-derived fuel gas, methane or natural gas, eliminating the need
Phosphoric acid fuel cells (PAFC) for external reformers.
Phosphoric acid fuel cells (PAFCs) consist of an anode and a Disadvantages associated with MCFC units arise from using a
cathode made of a finely dispersed platinum catalyst on carbon liquid electrolyte rather than a solid and the requirement to inject
Figure 5: Phosphoric acid fuel cell (Fuelcellworks ) Figure 7: Molten carbonate fuel cell (Fuelcellworks )
3
3
energize | July 2022 | 73