Page 31 - Energize Issue 1 2023
P. 31
TECHNICAL
of reliability characteristics will be fulfilled temperatures on a battery cell are more severe in shortening service life than cooler
for all contemplated units, (e.g., same temperatures are in extending it.
type of batteries)”. 8 It is commonly accepted that for every 10°C rise in temperature continually applied to a
If we can paraphrase with a simple battery, the result is a reduction in battery life by approximately 50% (See Figure 1 below).
English translation, service life is “the Another “stress factor” that can severely affect service life is undercharging or
actual battery life experienced from a cell overcharging the battery. Undercharging the cells will lead to plate sulfation with a
or group of cells under actual installed resultant build-up in internal resistance within the cell while reducing capacity and
conditions.” eventually shortened battery life. Conversely, overcharging the cells leads to accelerated
positive plate corrosion, and eventually shortened battery life as well.
It is important to understand at the
outset, there are several things that affect Accelerated life testing
service life: The US Nuclear Regulatory Commission accepts a VLA stationary battery for installation in
• Temperature – probably one of the Class 1E environments at a nuclear power station when the battery manufacturer qualifies
most important factors his battery following the IEEE 535-2013 standard. Accelerated Life Testing is an accepted
• Frequency and depth of discharges method to verify its design life. 9
• Maintenance practices – considered It does add a level of cycling, especially when qualifying a battery for greater than 8
by many to be a root cause of many hours, in that a modified performance test must be performed at 2-year intervals (and
failures annually for the last 25% of the testing period) to validate its ability to remain at ≥80% of
• Lack of understanding the true load capacity. 10
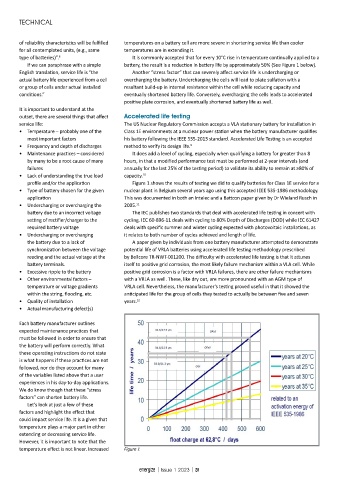
profile and/or the application Figure 1 shows the results of testing we did to qualify batteries for Class 1E service for a
• Type of battery chosen for the given nuclear plant in Belgium several years ago using this accepted IEEE 535-1986 methodology.
application This was documented in both an Intelec and a Battcon paper given by Dr Wieland Rusch in
• Undercharging or overcharging the 2005. 11
battery due to an incorrect voltage The IEC publishes two standards that deal with accelerated life testing in concert with
setting of rectifier/charger to the cycling. IEC 60-896-11 deals with cycling to 80% Depth of Discharges (DOD) while IEC 61427
required battery voltage deals with specific summer and winter cycling expected with photovoltaic installations, as
• Undercharging or overcharging it relates to both number of cycles achieved and length of life.
the battery due to a lack of A paper given by individuals from one battery manufacturer attempted to demonstrate
synchronization between the voltage potential life of VRLA batteries using accelerated life testing methodology prescribed
reading and the actual voltage at the by Bellcore TR-NWT-001200. The difficulty with accelerated life testing is that it attunes
battery terminals. itself to positive grid corrosion, the most likely failure mechanism within a VLA cell. While
• Excessive ripple to the battery positive grid corrosion is a factor with VRLA failures, there are other failure mechanisms
• Other environmental factors – with a VRLA as well. These, like dry out, are more pronounced with an AGM type of
temperature or voltage gradients VRLA cell. Nevertheless, the manufacturer’s testing proved useful in that it showed the
within the string, flooding, etc. anticipated life for the group of cells they tested to actually be between five and seven
• Quality of installation years. 12
• Actual manufacturing defect(s)
Each battery manufacturer outlines
expected maintenance practices that
must be followed in order to ensure that
the battery will perform correctly. What
these operating instructions do not state
is what happens if these practices are not
followed, nor do they account for many
of the variables listed above that a user
experiences in his day-to-day applications.
We do know though that these “stress
factors” can shorten battery life.
Let’s look at just a few of these
factors and highlight the effect that
could impact service life. It is a given that
temperature plays a major part in either
extending or decreasing service life.
However, it is important to note that the
temperature effect is not linear. Increased Figure 1
energize | Issue 1 2023 | 31