Page 33 - EngineerIt August 2021
P. 33
MEASUREMENT
From Figure 1, it can be seen that HbO 2 absorbs more red light The Beer-Lambert law explains that light decays exponentially
(600 nm) and allows more infrared light (940 nm) to pass through. when travelling though absorptive material. This can be used
RHb absorbs more light at infrared wavelengths, which allows to determine the level of oxygenated haemoglobin to total
more red light to pass through than in HbO 2. haemoglobin.
The most basic pulse oximeter consists of two LED (one red
660 nm LED and one infrared (IR) 940 nm LED) and a single The intensity of light absorbed at the diastole and systole are
photodiode (PD) in a reflective or transmissive configuration (see related by:
Figure 4). The pulse oximeter will pulse the red LED and measure
the resulting signal on the PD. Repeat this for the IR LED and
finally with both LEDs off to get a baseline for any ambient
external light sources. This generates a photoplethysmography where α measures the absorption rate of light in atrial blood and
(PPG) signal for both wavelengths. d2 is the AC amplitude of the PPG signal (see Figure 3). I diastole is
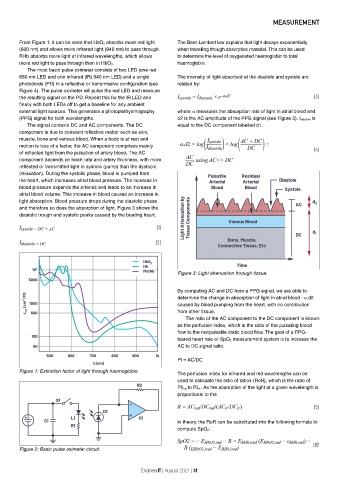
The signal contains DC and AC components. The DC equal to the DC component labelled d1.
component is due to constant reflective matter such as skin,
muscle, bone and venous blood. When a body is at rest and
motion is less of a factor, the AC component comprises mainly
of reflected light from the pulsation of artery blood. The AC
component depends on heart rate and artery thickness, with more
reflected or transmitted light in systolic (pump) than the dystopic
(relaxation). During the systolic phase, blood is pumped from
the heart, which increases atrial blood pressure. The increase in
blood pressure expands the arteries and leads to an increase in
atrial blood volume. This increase in blood causes an increase in
light absorption. Blood pressure drops during the diastolic phase
and therefore so does the absorption of light. Figure 3 shows the
diastolic trough and systolic peaks caused by the beating heart.
Figure 3: Light attenuation through tissue.
By computing AC and DC from a PPG signal, we are able to
determine the change in absorption of light in atrial blood –α.d2
caused by blood pumping from the heart, with no contribution
from other tissue.
The ratio of the AC component to the DC component is known
as the perfusion index, which is the ratio of the pulsating blood
flow to the nonpulsatile static blood flow. The goal of a PPG-
based heart rate or SpO 2 measurement system is to increase the
AC to DC signal ratio.
PI = AC/DC
Figure 1: Extinction factor of light through haemoglobin.
The perfusion index for infrared and red wavelengths can be
used to calculate the ratio of ratios (RoR), which is the ratio of
PIr ed to PL ir. As the absorption of the light at a given wavelength is
proportional to the
in theory, the RoR can be substituted into the following formula to
compute SpO 2:
Figure 2: Basic pulse oximeter circuit.
EngineerIT | August 2021 | 31