Page 35 - EngineerIT April 2022
P. 35
ELECTRONICS
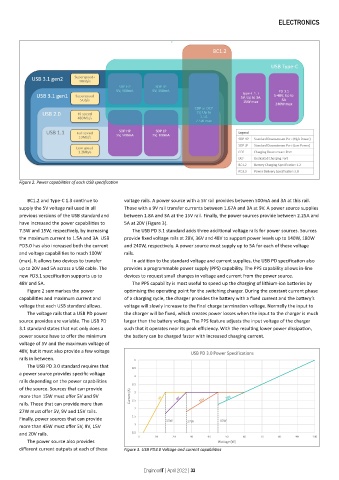
Figure 2. Power capabilities of each USB specification
BC1.2 and Type-C 1.3 continue to voltage rails. A power source with a 5V rail provides between 500mA and 3A at this rail.
supply the 5V voltage rail used in all Those with a 9V rail transfer currents between 1.67A and 3A at 9V. A power source supplies
previous versions of the USB standard and between 1.8A and 3A at the 15V rail. Finally, the power sources provide between 2.25A and
have increased the power capabilities to 5A at 20V (Figure 3).
7.5W and 15W, respectively, by increasing The USB PD 3.1 standard adds three additional voltage rails for power sources. Sources
the maximum current to 1.5A and 3A. USB provide fixed voltage rails at 28V, 36V and 48V to support power levels up to 140W, 180W
PD3.0 has also increased both the current and 240W, respectively. A power source must supply up to 5A for each of these voltage
and voltage capabilities to reach 100W rails.
(max). It allows two devices to transfer In addition to the standard voltage and current supplies, the USB PD specification also
up to 20V and 5A across a USB cable. The provides a programmable power supply (PPS) capability. The PPS capability allows in-line
new PD3.1 specification supports up to devices to request small changes in voltage and current from the power source.
48V and 5A. The PPS capability is most useful to speed up the charging of lithium-ion batteries by
Figure 2 summarises the power optimising the operating point for the switching charger. During the constant current phase
capabilities and maximum current and of a charging cycle, the charger provides the battery with a fixed current and the battery’s
voltage that each USB standard allows. voltage will slowly increase to the final charge termination voltage. Normally the input to
The voltage rails that a USB PD power the charger will be fixed, which creates power losses when the input to the charger is much
source provides are variable. The USB PD larger than the battery voltage. The PPS feature adjusts the input voltage of the charger
3.1 standard states that not only does a such that it operates near its peak efficiency. With the resulting lower power dissipation,
power source have to offer the minimum the battery can be charged faster with increased charging current.
voltage of 5V and the maximum voltage of
48V, but it must also provide a few voltage
rails in between.
The USB PD 3.0 standard requires that
a power source provides specific voltage
rails depending on the power capabilities
of the source. Sources that can provide
more than 15W must offer 5V and 9V
rails. Those that can provide more than
27W must offer 5V, 9V and 15V rails.
Finally, power sources that can provide
more than 45W must offer 5V, 9V, 15V
and 20V rails.
The power source also provides
different current outputs at each of these Figure 3. USB PD3.0 Voltage and current capabilities
EngineerIT | April 2022 | 33