Page 11 - Issue 3 2023
P. 11
INFRASTRUCTURE
How to build a 24 GHz FMCW
radar system
By Alex Andrews, Applications Engineer
his article serves as an introduction
to frequency modulated continuous
Twave (FMCW) radar generation
within the 24 GHz ISM band. It includes
the major building blocks required for
this type of radar system such as ramp
generation, transmit and receive stages,
down conversion and sampling.
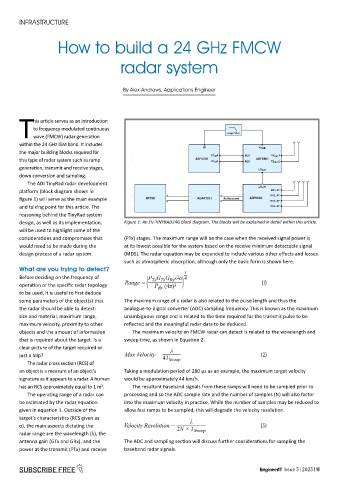
The ADI TinyRad radar development
platform (block diagram shown in
figure 1) will serve as the main example
and talking point for this article. The
reasoning behind the TinyRad system
design, as well as its implementation, Figure 1: An EV-TINYRAD24G block diagram. The blocks will be explained in detail within this article.
will be used to highlight some of the
considerations and compromises that (PTx) stages. The maximum range will be the case when the received signal power is
would need to be made during the at its lowest possible for the system based on the receive minimum detectable signal
design process of a radar system. (MDS). The radar equation may be expanded to include various other effects and losses
such as atmospheric absorption, although only the basic form is shown here.
What are you trying to detect?
Before deciding on the frequency of
operation or the specific radar topology
to be used, it is useful to first deduce
some parameters of the object(s) that The maximum range of a radar is also related to the pulse length and thus the
the radar should be able to detect: analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) sampling frequency. This is known as the maximum
size and material, maximum range, unambiguous range and is related to the time required for the transmit pulse to be
maximum velocity, proximity to other reflected and the meaningful radar data to be deduced.
objects and the amount of information The maximum velocity an FMCW radar can detect is related to the wavelength and
that is required about the target. Is a sweep time, as shown in Equation 2.
clear picture of the target required or
just a blip?
The radar cross section (RCS) of
an object is a measure of an object’s Taking a modulation period of 280 µs as an example, the maximum target velocity
signature as it appears to a radar. A human would be approximately 44 km/h.
has an RCS approximately equal to 1 m². The resultant baseband signals from these ramps will need to be sampled prior to
The operating range of a radar can processing and so the ADC sample rate and the number of samples (N) will also factor
be estimated by the radar equation into the maximum velocity in practice. While the number of samples may be reduced to
given in equation 1. Outside of the allow fast ramps to be sampled, this will degrade the velocity resolution.
target’s characteristics (RCS given as
σ), the main aspects dictating the
radar range are the wavelength (λ), the
antenna gain (GTx and GRx), and the The ADC and sampling section will discuss further considerations for sampling the
power at the transmit (PTx) and receive baseband radar signals.
SUBSCRIBE FREE EngineerIT Issue 3 | 2023 | 11