Page 39 - Energize March 2021
P. 39
TECHNICAL
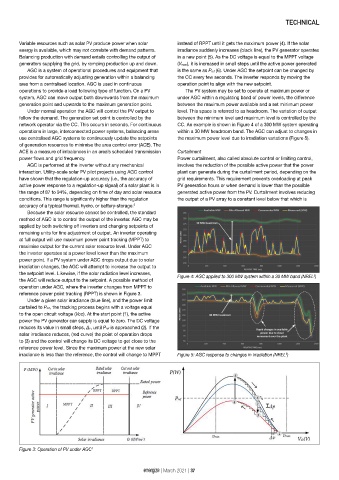
Variable resources such as solar PV produce power when solar instead of RPPT until it gets the maximum power (4). If the solar
energy is available, which may not correlate with demand patterns. irradiance suddenly increases (black line), the PV generator operates
Balancing production with demand entails controlling the output of in a new point (5). As the DC voltage is equal to the MPPT voltage
generators supplying the grid, by ramping production up and down. (Vmpp), it is increased in small steps until the active power generated
AGC is a system of operational procedures and equipment that is the same as Pref (6). Under AGC the setpoint can be changed by
provides for automatically adjusting generation within a balancing the CC every few seconds. The inverter responds by moving the
area from a centralised location. AGC is used in continuous operation point to align with the new setpoint.
operations to provide a load following type of function. On a PV The PV system may be set to operate at maximum power or
system, AGC can move output both downwards from the maximum under AGC within a regulating band of power levels, the difference
generation point and upwards to the maximum generation point. between the maximum power available and a set minimum power
Under normal operation the AGC will control the PV output to level. This space is referred to as headroom. The variation of output
follow the demand. The generation set point is controlled by the between the minimum level and maximum level is controlled by the
network operator via the CC. This occurs in seconds. For continuous CC. An example is shown in Figure 4 of a 300 MW system operating
operations in large, interconnected power systems, balancing areas within a 30 MW headroom band. The AGC can adjust to changes in
use centralised AGC systems to continuously update the setpoints the maximum power level due to irradiation variations (Figure 5).
of generation resources to minimise the area control error (ACE). The
ACE is a measure of imbalances in an area’s scheduled transmission Curtailment
power flows and grid frequency. Power curtailment, also called absolute control or limiting control,
AGC is performed at the inverter without any mechanical involves the reduction of the possible active power that the power
interaction. Utility-scale solar PV pilot projects using AGC control plant can generate during the curtailment period, depending on the
have shown that the regulation-up accuracy (i.e., the accuracy of grid requirements. This requirement prevents overloading at peak
active power response to a regulation-up signal) of a solar plant is in PV generation hours or when demand is lower than the possible
the range of 87 to 94%, depending on time of day and solar resource generated active power from the PV. Curtailment involves reducing
conditions. This range is significantly higher than the regulation the output of a PV array to a constant level below that which is
accuracy of a typical thermal, hydro, or battery-storage. 5
Because the solar resource cannot be controlled, the standard
method of AGC is to control the output of the inverter. AGC may be
applied by both switching off inverters and changing setpoints of
remaining units for fine adjustment of output. An inverter operating
at full output will use maximum power point tracking (MPPT) to
maximise output for the current solar resource level. Under AGC
the inverter operates at a power level lower than the maximum
power point. If a PV system under AGC drops output due to solar
irradiation changes, the AGC will attempt to increase the output to
the setpoint level. Likewise, if the solar radiation level increases,
5
Figure 4: AGC applied to 300 MW system within a 30 MW band (NREL )
the AGC will reduce output to the setpoint. A possible method of
operation under AGC, where the inverter changes from MPPT to
reference power point tracking (RPPT) is shown in Figure 3.
Under a given solar irradiance (blue line), and the power limit
curtailed to Pref, the tracking process begins with a voltage equal
to the open circuit voltage (Voc). At the start point (1), the active
power the PV generator can supply is equal to zero. The DC voltage
reduces its value in small steps, Δv, until Pref is approached (2). If the
solar irradiance reduces, (red curve) the point of operation drops
to (3) and the control will change its DC voltage to get close to the
reference power level. Since the maximum power at the new solar
5
irradiance is less than the reference, the control will change to MPPT Figure 5: AGC response to changes in irradiation (NREL )
Figure 3: Operation of PV under AGC 1
energize | March 2021 | 37