Page 37 - Energize May 2021
P. 37
TECHNICAL
A fully developed microgrid has the studying one-of-a-kind ice cores from the Arctic will lose ancient history if the cores melt; and
capability of automatically disconnecting data centres that process millions of financial transactions daily require constant power to
and operating independently from ensure the flow of capital.
the main grid. For example, if a storm
disrupts energy service from the main Incentives
grid, automated controls will reduce Government incentives for energy efficiency, renewable power generation and electric vehicle
non-critical loads (selected lighting, HVAC infrastructure all stimulate investment in advanced energy infrastructure.
systems, etc.) and the microgrid will
distribute power from on-site generation Benefits to energy consumers
and storage for an extended period of Reliability
time. When the main grid is back online, Energy consumers have high expectations for reliable, high quality electricity but they don’t
the microgrid will automatically reconnect, expect to pay a lot for it. They need the lights to stay on, production lines to keep running
recharge energy storage, and ramp and energy costs to be low. Increasing the amount of on-site energy (generation and/or
down on-site generation as appropriate. storage) with a microgrid solution reduces the risk of a catastrophic power loss and may
Microgrids will get approximately 20 to lower costs.
25% of their on-site power generation
from renewable technologies integrated Efficiency
with thermal energy storage and electric Lowering consumption is the fastest way to impact energy costs. A first step is creating
battery storage if cost competitive. transparency throughout the system with advanced metering to drive savings – “what gets
measured gets managed.” Implementing other technologies, such as energy efficient lighting,
Market drivers variable frequency drives (VFDs) on motors and chiller/boiler upgrades, will further improve
The key factors influencing the energy efficiency. Increasing the amount of on-site generation has the added advantage of
emergence of microgrid solutions are the minimising transmission and distribution line losses.
vulnerability of energy infrastructure to
cyber threats, growing energy demand, Security of supply
the need for reliable and secure power, Energy supply is vulnerable to acts of terrorism, natural disasters, and other risks. Increasing
and external incentives. the amount of on-site generation in conjunction with appropriate physical and cyber security
measures is a risk mitigation strategy.
Cyber security
As the reliance on modern Sustainability
communication technology increases A growing number of organisations place a higher value on renewable energy generation and
(wireless, cloud computing), power are committing to long-term targets, regardless of the expected time to recoup the investment.
systems are vulnerable to cyber-attacks For example, a university may want to serve as a “living laboratory” for environmental
and hackers. In some specific customer engineering and technology developed by its students and researchers, or a manufacturer
segments, such as the military and may want to increase its Dow Jones Sustainability Index score by reducing GHG in their
research labs, there is significant value in production processes.
a secure network.
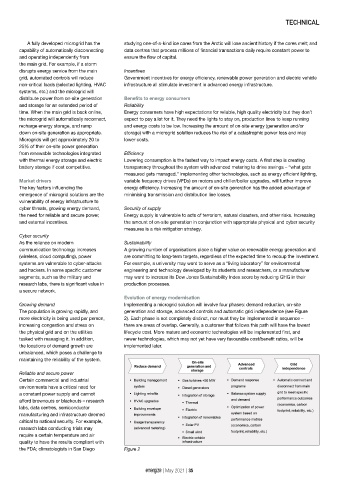
Evolution of energy modernisation
Growing demand Implementing a microgrid solution will involve four phases: demand reduction, on-site
The population is growing rapidly, and generation and storage, advanced controls and automatic grid independence (see Figure
more electricity is being used per person, 2). Each phase is not completely distinct, nor must they be implemented in sequence –
increasing congestion and stress on there are areas of overlap. Generally, a customer that follows this path will have the lowest
the physical grid and on the utilities lifecycle cost. More mature and economic technologies will be implemented first, and
tasked with managing it. In addition, newer technologies, which may not yet have very favourable cost/benefit ratios, will be
the locations of demand growth are implemented later.
unbalanced, which poses a challenge to
maintaining the reliability of the system.
Reliable and secure power
Certain commercial and industrial
environments have a critical need for
a constant power supply and cannot
afford brownouts or blackouts – research
labs, data centres, semiconductor
manufacturing and infrastructure deemed
critical to national security. For example,
research labs conducting trials may
require a certain temperature and air
quality to have the results compliant with
the FDA; climatologists in San Diego Figure 2
energize | May 2021 | 35