Page 48 - Energize June 2021
P. 48
TECHNICAL
Passive arc-resistant switchgear
Passive arc-resistant equipment attempts to contain the AF within
the body of the switchgear, and typically provides increased
protection through strengthened enclosures and the venting of
pressurized hot gases and other arc products. Additional protection
on LV switchgear can be provided by solid insulation on all exposed
conductors such as busbars connection points, etc.
Active arc-resistant switchgear and techniques
One drawback of passive arc-resistant switchgear is that while it
provides a significant degree of protection to workers, it may not
do anything to reduce the intensity or duration of the internal arcing
fault itself. The equipment may be designed to contain the blast, but
the internal damage may be significant, requiring either re-work or
replacement of the switchgear. Active arc-resistant or arc reduction
(AR) switchgear is equipment designed to reduce incident energy,
shorten clearing times, or redirect energy away from the arc.
Figure 2: Operation of current limiting fuse (Eaton)
AR switchgear systems use devices that limit the energy in
the arc by limiting the current flowing or the duration of the arc.
The devices may be incorporated in the body of the switch or an optimal balance between arc flash reduction and maximizing
be mounted externally. Placing a device that limits arc energy in selectivity. This requires that arc flash be considered as part of the
non-arc-resistant switchgear could meet the requirements for arc device. When replacing thermal-magnetic breakers with devices
resistant switchgear. which have an electronic trip unit, or upgrading older trip units with
modern trip units, it would make good sense to add the IT setting
Current limiting devices to the operating portfolio.
The extent of an AF can be reduced by limiting the current flowing in
the arc circuit by current-limiting fuses or reactors. Current-limiting Arc flash reduction maintenance system (ARMS)
fuses act very quickly when the fault current levels are high enough This is deployed as a part of the internal trip unit of air circuit
to cause the fuse to respond in its current-limiting region. Current- breakers. The protection curve in any low voltage air circuit breaker
limiting fuses operate by creating additional arcs within the fuse trip unit allows settings of variable time and instantaneous operation
structure, increasing the voltage across the fuse and decreasing for selective coordination. ARMS offers a separate protection
the voltage across the arc. For normal fault currents the fuse takes setting that, when enabled in the maintenance mode, overrides the
several cycles to operate. Current is limited by the fuse operating standard settings and reverts to a predetermined instantaneous
before the maximum possible peak current is reached (Figure 2). trip setting. The advantage of this is a significant reduction in total
clearing time, which in turn reduces the arc flash hazard.
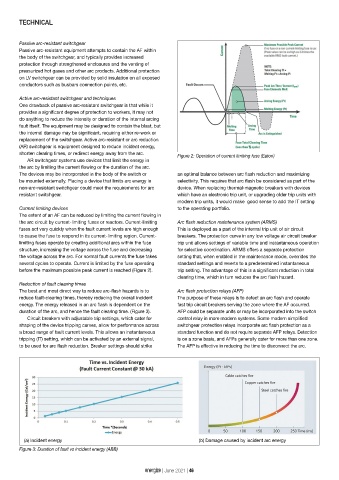
Reduction of fault clearing times
The best and most direct way to reduce arc-flash hazards is to Arc flash protection relays (AFP)
reduce fault-clearing times, thereby reducing the overall incident The purpose of these relays is to detect an arc flash and operate
energy. The energy released in an arc flash is dependent on the fast trip circuit breakers serving the zone where the AF occurred.
duration of the arc, and hence the fault clearing time. (Figure 3). AFP could be separate units or may be incorporated into the switch
Circuit breakers with adjustable trip settings, which cater for control relay in more modern systems. Some modern simplified
shaping of the device tripping curves, allow for performance across switchgear protection relays incorporate arc flash protection as a
a broad range of fault current levels. This allows an instantaneous standard function and do not require separate AFP relays. Detection
tripping (IT) setting, which can be activated by an external signal, is on a zone basis, and AFPs generally cater for more than one zone.
to be used for arc flash reduction. Breaker settings should strike The AFP is effective in reducing the time to disconnect the arc.
(a) Incident energy (b) Damage caused by incident arc energy
Figure 3: Duration of fault vs incident energy (ABB)
energize | June 2021 | 46