Page 47 - Energize August 2021
P. 47
TECHNICAL
increasing fuel consumption and decreasing power. Low SAPS
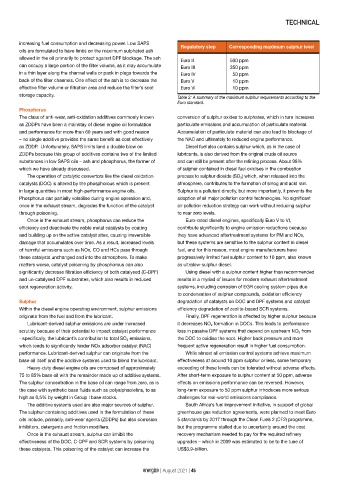
Regulatory step Corresponding maximum sulphur level
oils are formulated to have limits on the maximum sulphated ash
allowed in the oil primarily to protect against DPF blockage. The ash
Euro II 500 ppm
can occupy a large portion of the filter volume, as it may accumulate Euro III 350 ppm
in a thin layer along the channel walls or pack in plugs towards the Euro IV 50 ppm
back of the filter channels. One effect of the ash is to decrease the Euro V 10 ppm
effective filter volume or filtration area and reduce the filter’s soot Euro VI 10 ppm
storage capacity.
Table 2: A summary of the maximum sulphur requirements according to the
Euro standard.
Phosphorus
The class of anti-wear, anti-oxidation additives commonly known conversion of sulphur oxides to sulphates, which in turn increases
as ZDDPs have been a mainstay of diesel engine oil formulation particulate emissions and accumulation of particulate material.
and performance for more than 60 years and with good reason Accumulation of particulate material can also lead to blockage of
– no single additive provides the same benefit as cost effectively the NAC and ultimately to reduced engine performance.
as ZDDP. Unfortunately, SAPS limits land a double blow on Diesel fuel also contains sulphur which, as in the case of
ZDDPs because this group of additives contains two of the limited lubricants, is also derived from the original crude oil source
substances in low SAPS oils – ash and phosphorus, the former of and can still be present after the refining process. About 98%
which we have already discussed. of sulphur contained in diesel fuel oxidises in the combustion
The operation of catalytic convertors like the diesel oxidation process to sulphur dioxide (SO₂) which, when released into the
catalysts (DOC) is altered by the phosphorous which is present atmosphere, contributes to the formation of smog and acid rain.
in large quantities in most high-performance engine oils. Sulphur is a pollutant directly, but more importantly, it prevents the
Phosphorus can partially volatilise during engine operation and, adoption of all major pollution control technologies. No significant
once in the exhaust stream, degrades the function of the catalyst air pollution reduction strategy can work without reducing sulphur
through poisoning. to near zero levels.
Once in the exhaust stream, phosphorus can reduce the Euro-rated diesel engines, specifically Euro V to VI,
efficiency and deactivate the noble metal catalysts by coating contribute significantly to engine emission reductions because
and building up on the active catalyst sites, causing irreversible they have advanced aftertreatment systems for PM and NOx,
damage that accumulates over time. As a result, increased levels but these systems are sensitive to the sulphur content in diesel
of harmful emissions such as NOx, CO and HCs pass through fuel, and for this reason, most engine manufacturers have
these catalysts unchanged and into the atmosphere. To make progressively limited fuel sulphur content to 10 ppm, also known
matters worse, catalyst poisoning by phosphorous can also as ultralow-sulphur diesel.
significantly decrease filtration efficiency of both catalysed (C-DPF) Using diesel with a sulphur content higher than recommended
and un-catalysed DPF substrates, which also results in reduced results in a myriad of issues for modern exhaust aftertreatment
soot regeneration activity. systems, including corrosion of EGR cooling system pipes due
to condensation of sulphur compounds, oxidation efficiency
Sulphur degradation of catalysts on DOC and DPF systems and catalyst
Within the diesel engine operating environment, sulphur emissions efficiency degradation of zeolite-based SCR systems.
originate from the fuel and from the lubricant. Finally, DPF regeneration is affected by higher sulphur because
Lubricant-derived sulphur emissions are under increased it decreases NO₂ formation in DOCs. This leads to performance
scrutiny because of their potential to impact catalyst performance loss in passive DPF systems that depend on upstream NO₂ from
- specifically, the lubricant’s contribution to total SO₂ emissions, the DOC to oxidise the soot. Higher back pressure and more
which tends to significantly hinder NOx adsorber catalyst (NAC) frequent active regeneration result in higher fuel consumption.
performance. Lubricant-derived sulphur can originate from the While almost all emission control systems achieve maximum
base oil itself and the additive systems used to blend the lubricant. effectiveness at around 10 ppm sulphur or less, some temporary
Heavy-duty diesel engine oils are composed of approximately exceeding of these levels can be tolerated without adverse effects.
75 to 85% base oil with the remainder made up of additive systems. After short-term exposure to sulphur content at 50 ppm, adverse
The sulphur concentration in the base oil can range from zero, as is effects on emissions performance can be reversed. However,
the case with synthetic base fluids such as polyalphaolefins, to as long-term exposure to 50 ppm sulphur introduces more serious
high as 0,5% by weight in Group I base stocks. challenges for real-world emissions compliance.
The additive systems used are also major sources of sulphur. South Africa’s fuel improvement initiative, in support of global
The sulphur-containing additives used in the formulation of these greenhouse gas reduction agreements, were planned to meet Euro
oils include, primarily, anti-wear agents (ZDDPs) but also corrosion 5 standards by 2017 through the Clean Fuels 2 (CF2) programme,
inhibitors, detergents and friction modifiers. but the programme stalled due to uncertainty around the cost
Once in the exhaust stream, sulphur can inhibit the recovery mechanism needed to pay for the required refinery
effectiveness of the DOC, C-DPF and SCR systems by poisoning upgrades – which in 2009 was estimated to be to the tune of
these catalysts. This poisoning of the catalyst can increase the US$3,9-billion.
energize | August 2021 | 45