Page 50 - Energize August 2021
P. 50
TECHNICAL
Hybrid renewable energy power
systems: A growing sector
by Mike Rycroft, Now Media
Hybrid power systems have historically been confined to small off-grid systems or more recently,
microgrids. The decreasing cost of bulk location-independent electricity storage is leading to the increased
appearance of larger private and utility scale hybrid systems. The first South African hybrid power producer
contracted to supply dispatchable power is on the cards, and more are likely to follow.
ybrid renewable energy (RE) Possible criteria:
systems have been used for • Cost of electricity: The hybrid unit electricity cost is lower than that produced by the
Hmany years to provide power to components acting on their own.
sites remote from the grid, or where grid • Security of supply: Availability and reliability of supply is greater than that of the
connection was uneconomical. Typical components acting on their own.
applications were remote, low-power
telecommunications sites, where the hybrid To achieve this requires that the performance of the individual units is complementary to
consisted of solar PV plus batteries, or each other. The suitability of a hybrid combination will depend on the complementarity of the
small wind turbines plus batteries. different resources.
At one stage, Telkom had 15 000 Most existing hybrids are based on collocation of resources servicing a single consumer.
of these sites in operation around the With today’s smart grid technology and the emergence of both renewable generation and bulk
country. In more recent years, larger hybrid storage at grid level, the definition becomes less clear. Microgrids, for instance, operate on the
systems have been used to provide power hybrid principle, where there is only one primary source of energy combined with storage, as
to remote villages. Even larger systems in remote village electrification.
are used to power remote mines and The virtual power station concept allows the hybridisation of non-collocated resources.
agricultural complexes. The decreasing The national grid is in fact a hybrid of renewable and non-renewable resources, combined with
costs of renewable energy components energy storage. This article will be confined to plant consisting of collocated resources and will
and bulk electricity storage and the consider systems ranging from domestic hybrids to utility scale hybrids.
maturity of the associated technology
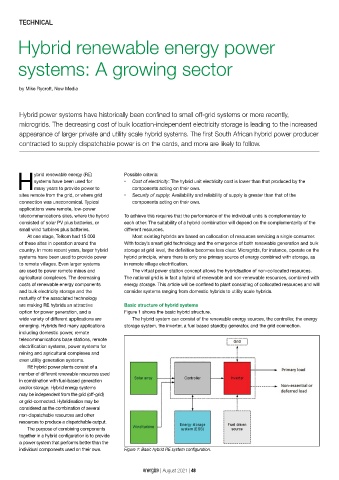
are making RE hybrids an attractive Basic structure of hybrid systems
option for power generation, and a Figure 1 shows the basic hybrid structure.
wide variety of different applications are The hybrid system can consist of the renewable energy sources, the controller, the energy
emerging. Hybrids find many applications storage system, the inverter, a fuel based standby generator, and the grid connection.
including domestic power, remote
telecommunications base stations, remote
electrification systems, power systems for
mining and agricultural complexes and
even utility generation systems.
RE hybrid power plants consist of a
number of different renewable resources used
in combination with fuel-based generation
and/or storage. Hybrid energy systems
may be independent from the grid (off-grid)
or grid-connected. Hybridisation may be
considered as the combination of several
non-dispatchable resources and other
resources to produce a dispatchable output.
The purpose of combining components
together in a hybrid configuration is to provide
a power system that performs better than the
individual components used on their own. Figure 1: Basic hybrid RE system configuration.
energize | August 2021 | 48