Page 59 - Energize October 2021
P. 59
TECHNICAL
In a new cable the voltage and current in the cable under test none of the results can be related to the IEC method. These methods,
will be close to 90° out of phase due to the high resistance of the which are more suitable for on-line monitoring and measurement,
insulation, and tan δ value will be low. As the insulation ages, the include the use of HF transformers, piezo devices and acoustics. The
angle will decrease and tan δ becomes higher and becomes more HF transformer and coupling capacitor methods are the most reliable
voltage dependent. Water trees exhibit a capacitance that increases when it comes to on line measurement. 2
with voltage, so the tan delta measurements taken at higher voltage
increase (see Figure 5). This plays an important part in analysing Background noise
cable condition. 3 A major challenge is that PD energy quantities are usually minute
compared to the ambient or background noise. If PD current is the
parameter being measured, a typical PD event involves several tens of
pico-Coulomb (pC) charge transfer in tens of microseconds, and the PD
current pulse magnitude can be in the order of one μA. Measurement
of such a minute current in an environment of typical power system
load currents and electromagnetic interferences is problematic, and
extraction of PD signals from the noisy environment is a major frontier
of research in PD technology. Significant progress, however, has
been achieved in developing effective techniques of noise mitigation
in PD diagnosis. In that regard most commercial PD measurement
technologies have state-of the art PD noise management although
there is still room for improvement.
Key parameters for PD analysis
The following are the main parameters used in PD analysis:
• PD count: The number of PD incidents occurring during the test.
Figure 5: Effect of age and voltage on Tan delta measurements 5 • PD intensity: The level of the PD discharge for each incident
• Partial discharge inception voltage (PDIV): This is the voltage at
Partial discharge (PD) testing which PD events start to occur. It has been shown that PDIV is a
Partial discharge, or PD, is caused by local electrical stress in the function of test voltage frequency or the rate of change of voltage
insulation or on the surface of the insulation in electrical equipment. (dU/dt), in the region of the zero crossing during polarity reversal.
It not only indicates insulation defects but it is also responsible The inception voltage for surface discharges and internal discharges
for developing them. PD is therefore a good indicator of dielectric in layered interfaces, like splices and terminations, is particularly
condition and is present well in advance of insulation failure. PD is the sensitive to the voltage gradient. 2
predator of insulation. Once damage has started it cannot be stopped. • Partial discharge extinction voltage (PDEV): This is the voltage at
Partial discharges are often regarded as both symptoms and agencies which an existing PD event extinguishes. There is no known direct
of power cable degradation. correlation between PDIV and PDEV, but the parameters follow a
Power cable failures account for most of power distribution system hysteresis pattern. Empirical observations and practical experience
failures, and most are caused by partial discharge activity in power indicate that PDEV levels are typically between 0,8 and 0,9 times
cable accessories. Improved reliability of power cable systems entails PDIV and sometimes as low as 0,7 times. It has been found that PD
1
early detection and mitigation of incipient PD faults. The recommended activity extinguishes with very slow dU/dt, which makes it difficult to
method (IEC 60750) of PD testing involves detection and measurement conduct PD measurements using low frequencies like 0,1 Hz. Only a
of PD discharge currents. The method is offline and involves the use of damped oscillating voltage source (DAC) can properly measure PDIV
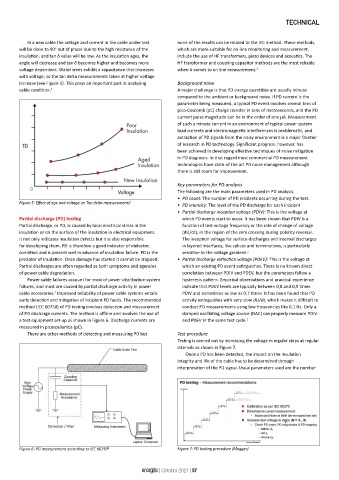
a test equipment set-up as shown in Figure 6. Discharge currents are and PDEV in the same test cycle. 2
measured in picocoulombs (pC).
There are other methods of detecting and measuring PD but Test procedure
Testing is carried out by increasing the voltage in regular steps at regular
intervals as shown in Figure 7.
Once a PD has been detected, the impact on the insulation
integrity and life of the cable has to be determined through
interpretation of the PD signal. Usual parameters used are the number
Figure 6: PD measurement according to IEC 60750 4 Figure 7: PD testing procedure (Megger)
energize | October 2021 | 57