Page 58 - Energize October 2021
P. 58
TECHNICAL
required time. This gives a 97% probability that the cable will be good The tested MV cable must withstand the AC test voltage for the
for at least another two years. The cable fails if a fault develops during specified testing time without flashover or insulation breakdown. A
1
the test period. This is in fact a good result as a potential fault has been typical VLF withstand test is performed with voltages between two
identified, allowing the cable to be repaired or replaced, before an in- and three times Uo for the maximum period of one hour. Because
service failure occurs. AC testing is important to detect failures that are VLF testing is covered in a number of different standards (IEC, IEEE,
dependent on the rate of change of voltage, such as those occurring at Cenelec), and has an easy application on site, it has become a widely
insulation layer interfaces. adopted method. 1
The simple result (Pass/Fail) only shows that the cable was either
Grid frequency (50 Hz) testing ready for operation, or damaged at the time of testing, and provides
This system applies a higher-than-normal voltage at the grid frequency no estimate of how long the cable can remain in operation, nor when
to the cable for an extended time period. Although this simulates real the next check should be performed. For this reason, diagnostic
operating conditions, high power levels are required for long cables, methods like tan-delta or partial discharge measurement have
leading to large equipment sizes. become more popular. 1
Very low frequency (VLF) AC Tan delta testing
VLF testing is preferred over mains grid frequency testing, as the Tan δ is used as a maintenance test to record the varying overall
waveforms used can apply the same level of voltage change rate as condition of the cable insulation, rather than cable insulation failure.
grid, but with smaller equipment. The frequencies used are in the range The test relies on the fact that deterioration of insulation resistance will
0,01 Hz to 1 Hz, with 0,1 Hz emerging as the most commonly used. Two result in a change of the phase angle between voltage and current in a
different waveforms are in use: The cosine rectangular waveform (CRW) cable. The test is conducted offline and a chosen waveform is applied
and the sine wave. The CRW is illustrated in Figure 2. to the cable. An MV cable can be represented as a parallel combination
of resistance and capacitance, where the capacitance is the cable
capacitance and the resistance the insulation resistance.
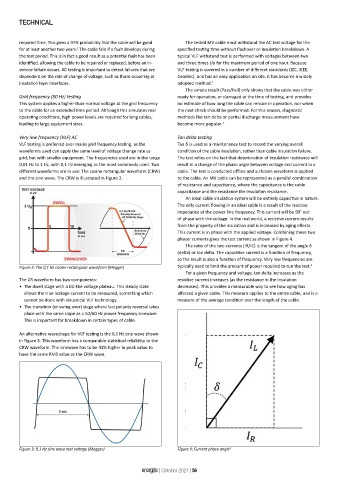
An ideal cable insulation system will be entirely capacitive in nature.
The only current flowing in an ideal cable is a result of the reactive
impedance at the power line frequency. This current will be 90° out
of phase with the voltage. In the real world, a resistive current results
from the property of the insulation and is increased by aging effects.
This current is in phase with the applied voltage. Combining these two
phasor currents gives the test current as shown in Figure 4.
The ratio of the two currents (IR/IC) is the tangent of the angle δ
(delta) or tan delta. The capacitive current is a function of frequency,
so the result is also a function of frequency. Very low frequencies are
Figure 2: The 0,1 Hz cosine rectangular waveform (Megger) typically used to limit the amount of power required to run the test. 3
For a given frequency and voltage, tan delta increases as the
The CR waveform has two components: resistive current increases (as the resistance in the insulation
• The dwell stage with a DC-like voltage plateau. This steady state decreases). This provides a measurable way to see how aging has
allows the true leakage current to be measured, something which affected a given cable. This measure applies to the entire cable, and is a
cannot be done with sinusoidal VLF technology. measure of the average condition over the length of the cable.
• The transition (or swing over) stage where fast polarity reversal takes
place with the same slope as a 50/60 Hz power frequency sinewave.
This is important for breakdown in certain types of cable.
An alternative waveshape for VLF testing is the 0,1 Hz sine wave shown
in Figure 3. This waveform has a comparable statistical reliability to the
CRW waveform. The sinewave has to be 41% higher in peak value to
have the same RMS value as the CRW wave.
Figure 3: 0,1 Hz sine wave test voltage (Megger) Figure 4: Current phase angle 4
energize | October 2021 | 56