Page 21 - Issue 3 2023
P. 21
TECHNICAL
Battery electric vehicles overview
Battery electric vehicles are becoming more common, although the market penetration is still
very low. Development has increased the single charge driving range, charging times have been
reduced, and other developments allow the integration of these vehicles with the smart grid.
By Mike Rycroft: Energize
he range of electric vehicles
extends from motorcycles to
Theavy duty trucks. This article
focuses on battery-powered private
passenger vehicles, or electric people
movers (EPMs) as they are now
commonly called.
Although the move to EPMs is being
driven mainly by government policies
and subsidies in an effort to reduce
harmful emissions, there are several
advantages including lower running
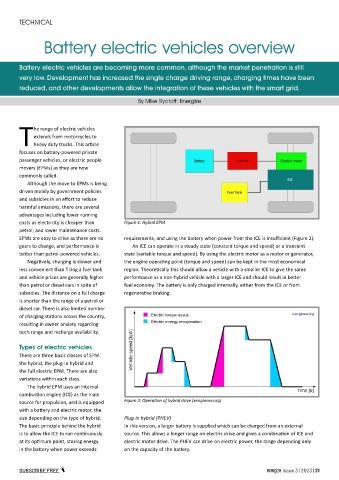
costs as electricity is cheaper than Figure 1: Hybrid EPM
petrol; and lower maintenance costs.
EPMs are easy to drive as there are no requirements, and using the battery when power from the ICE is insufficient (Figure 2).
gears to change, and performance is An ICE can operate in a steady state (constant torque and speed) or a transient
better than petrol-powered vehicles. state (variable torque and speed). By using the electric motor as a motor or generator,
Negatively, charging is slower and the engine operating point (torque and speed) can be kept in the most economical
less convenient than filling a fuel tank region. Theoretically this should allow a vehicle with a smaller ICE to give the same
and vehicle prices are generally higher performance as a non-hybrid vehicle with a larger ICE and should result in better
than petrol or diesel cars in spite of fuel economy. The battery is only charged internally, either from the ICE or from
subsidies. The distance on a full charge regenerative braking.
is shorter than the range of a petrol or
diesel car. There is also limited number
of charging stations across the country,
resulting in owner anxiety regarding
both range and recharge availability.
Types of electric vehicles
There are three basic classes of EPM:
the hybrid, the plug-in hybrid and
the full electric EPM. There are also
variations within each class.
The hybrid EPM uses an internal
combustion engine (ICE) as the main
source for propulsion, and is equipped Figure 2: Operation of hybrid drive (xengineer.org)
with a battery and electric motor, the
size depending on the type of hybrid. Plug-in hybrid (PHEV)
The basic principle behind the hybrid In this version, a larger battery is supplied which can be charged from an external
is to allow the ICE to run continuously source. This allows a longer range on electric drive and gives a combination of ICE and
at its optimum point, storing energy electric motor drive. The PHEV can drive on electric power, the range depending only
in the battery when power exceeds on the capacity of the battery.
SUBSCRIBE FREE energize Issue 3 | 2023 | 21