Page 21 - EngineerIT September 2021
P. 21
MEASUREMENT
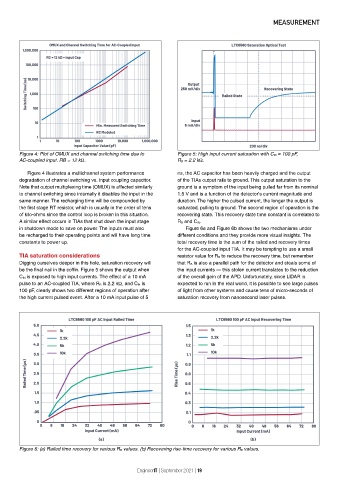
Figure 4: Plot of OMUX and channel switching time due to Figure 5: High input current saturation with C IN = 100 pF,
AC-coupled input. RB = 12 kΩ. R B = 2.2 kΩ.
Figure 4 illustrates a multichannel system performance ns, the AC capacitor has been heavily charged and the output
degradation of channel switching vs. input coupling capacitor. of the TIAs output rails to ground. This output saturation to the
Note that output multiplexing time (OMUX) is affected similarly ground is a symptom of the input being pulled far from its nominal
to channel switching since internally it disables the input in the 1.5 V and is a function of the detector’s current magnitude and
same manner. The recharging time will be compounded by duration. The higher the pulsed current, the longer the output is
the first stage RT resistor, which is usually in the order of tens saturated, pulling to ground. The second region of operation is the
of kilo-ohms since the control loop is broken in this situation. recovering state. This recovery state time constant is correlated to
A similar effect occurs in TIAs that shut down the input stage R B and C IN.
in shutdown mode to save on power. The inputs must also Figure 6a and Figure 6b shows the two mechanisms under
be recharged to their operating points and will have long time different conditions and they provide more visual insights. The
constants to power up. total recovery time is the sum of the railed and recovery times
for the AC-coupled input TIA. It may be tempting to use a small
TIA saturation considerations resistor value for R B to reduce the recovery time, but remember
Digging ourselves deeper in this hole, saturation recovery will that R B is also a parallel path for the detector and steals some of
be the final nail in the coffin. Figure 5 shows the output when the input currents – this stolen current translates to the reduction
C IN is exposed to high input currents. The effect of a 10 mA of the overall gain of the APD. Unfortunately, since LIDAR is
pulse to an AC-coupled TIA, where R B is 2.2 kΩ, and C IN is expected to run in the real world, it is possible to see large pulses
100 pF, clearly shows two different regions of operation after of light from other systems and cause tens of micro-seconds of
the high current pulsed event. After a 10 mA input pulse of 5 saturation recovery from nanosecond laser pulses.
Figure 6: (a) Railed time recovery for various R B values. (b) Recovering rise-time recovery for various R B values.
EngineerIT | September 2021 | 19