Page 12 - EngineerIT November 2022
P. 12
ELECTRONICS DESIGN
at V1 (inside the chop switches) and V2 (after the output • Glitches caused by charge injection mismatch of the
chop switches) in Figure 1. Additional glitch artifacts at even chopping switches and finite amplifier bandwidth at even
harmonics of the chop frequency are caused by finite amplifier multiples of the chopping frequency.
bandwidth as shown in Figure 5 (right).
System level considerations
As with ripple, amplifier designers have techniques to reduce When using a zero-drift amplifier in a data acquisition
the impact of glitches in zero-drift amplifiers: solution, it is important to understand where the frequency
• Charge injection trim: A trimmable charge can be injected artifacts are and plan for them accordingly.
into the inputs of a chopped amplifier to compensate for
charge mismatch, which reduces the amount of input Finding the chopping frequency in the data
current at the op amp’s inputs. sheet
• Multi-channel chopping: This not only reduces glitch The chopping frequency is usually explicitly stated in the data
magnitude but also moves it to a higher frequency, making sheet, but it can also be determined by looking at the noise
filtering easier. This technique results in more frequent spectrum plots. A couple of ADI’s latest zero-drift amplifier
glitches but with smaller magnitudes than simply chopping data sheets show where in the spectrum artifacts occur.
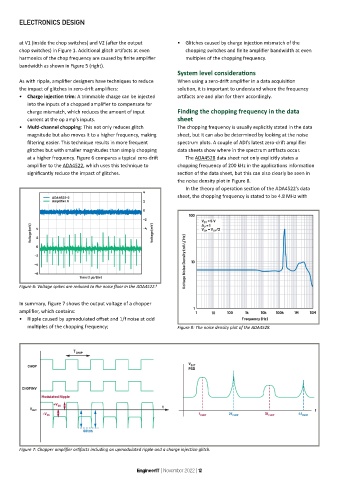
at a higher frequency. Figure 6 compares a typical zero-drift The ADA4528 data sheet not only explicitly states a
amplifier to the ADA4522, which uses this technique to chopping frequency of 200 kHz in the applications information
significantly reduce the impact of glitches. section of the data sheet, but this can also clearly be seen in
the noise density plot in Figure 8.
In the theory of operation section of the ADA4522’s data
sheet, the chopping frequency is stated to be 4.8 MHz with
Figure 6: Voltage spikes are reduced to the noise floor in the ADA4522. 8
In summary, Figure 7 shows the output voltage of a chopper
amplifier, which contains:
• Ripple caused by upmodulated offset and 1/f noise at odd
multiples of the chopping frequency; Figure 8: The noise density plot of the ADA4528.
Figure 7: Chopper amplifier artifacts including an upmodulated ripple and a charge injection glitch.
EngineerIT | November 2022 | 12