Page 13 - EngineerIT November 2022
P. 13
ELECTRONICS DESIGN
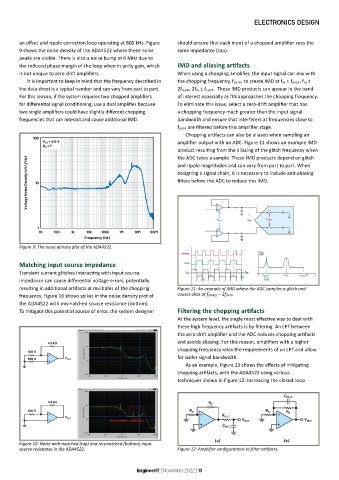
an offset and ripple correction loop operating at 800 kHz. Figure should ensure that each input of a chopped amplifier sees the
9 shows the noise density of the ADA4522 where these noise same impedance (top).
peaks are visible. There is also a noise bump at 6 MHz due to
the reduced phase margin of the loop when in unity gain, which IMD and aliasing artifacts
is not unique to zero-drift amplifiers. When using a chopping amplifier, the input signal can mix with
It is important to keep in mind that the frequency described in the chopping frequency, f CHOP, to create IMD at f IN ± f CHOP, f IN ±
the data sheet is a typical number and can vary from part to part. 2f CHOP, 2f IN ± f CHOP. These IMD products can appear in the band
For this reason, if the system requires two chopped amplifiers of interest especially as fIN approaches the chopping frequency.
for differential signal conditioning, use a dual amplifier because To eliminate this issue, select a zero-drift amplifier that has
two single amplifiers could have slightly different chopping a chopping frequency much greater than the input signal
frequencies that can interact and cause additional IMD. bandwidth and ensure that interferers at frequencies close to
f CHOP are filtered before this amplifier stage.
Chopping artifacts can also be aliased when sampling an
amplifier output with an ADC. Figure 11 shows an example IMD
product resulting from the aliasing of the glitch frequency when
the ADC takes a sample. These IMD products depend on glitch
and ripple magnitudes and can vary from part to part. When
designing a signal chain, it is necessary to include anti-aliasing
filters before the ADC to reduce this IMD.
Figure 9: The noise density plot of the ADA4522.
Matching input source impedance
Transient current glitches interacting with input source
impedance can cause differential voltage errors, potentially
resulting in additional artifacts at multiples of the chopping Figure 11: An example of IMD where the ADC samples a glitch and
frequency. Figure 10 shows spikes in the noise density plot of causes alias at f SAMPLE – 2f CHOP.
the ADA4522 with mismatched source resistance (bottom).
To mitigate this potential source of error, the system designer Filtering the chopping artifacts
At the system level, the single most effective way to deal with
these high frequency artifacts is by filtering. An LPF between
the zero-drift amplifier and the ADC reduces chopping artifacts
and avoids aliasing. For this reason, amplifiers with a higher
chopping frequency relax the requirements of an LPF and allow
for wider signal bandwidth.
As an example, Figure 13 shows the effects of mitigating
chopping artifacts, with the ADA4522 using various
techniques shown in Figure 12: increasing the closed-loop
Figure 10: Noise with matched (top) and mismatched (bottom) input
source resistance in the ADA4522. Figure 12: Amplifier configurations to filter artifacts.
EngineerIT | November 2022 | 13