Page 36 - Energize February 2021
P. 36
TECHNICAL
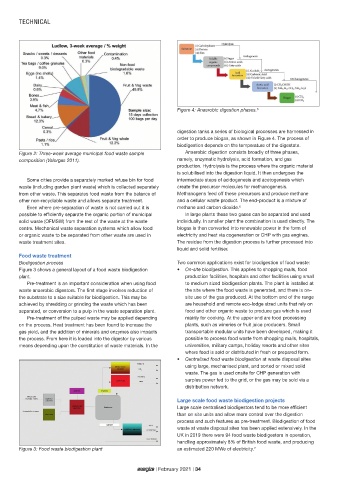
Figure 4: Anaerobic digestion phases. 6
digestion tanks a series of biological processes are harnessed in
order to produce biogas, as shown in Figure 4. The process of
biodigestion depends on the temperature of the digestate.
Figure 2: Three-week average municipal food waste sample Anaerobic digestion consists broadly of three phases,
composition (Valorgas 2011). namely, enzymatic hydrolysis, acid formation, and gas
production. Hydrolysis is the process where the organic material
is solubilised into the digestion liquid. It then undergoes the
Some cities provide a separately marked refuse bin for food intermediate steps of acidogenesis and acetogenesis which
waste (including garden plant waste) which is collected separately create the precursor molecules for methanogenesis.
from other waste. This separates food waste from the balance of Methanogens feed off these precursors and produce methane
other non-recyclable waste and allows separate treatment. and a cellular waste product. The end-product is a mixture of
Even where pre-separation of waste is not carried out it is methane and carbon dioxide. 6
possible to efficiently separate the organic portion of municipal In large plants these two gases can be separated and used
solid waste (OFMSW) from the rest of the waste at the waste individually. In smaller plant the combination is used directly. The
centre. Mechanical waste separation systems which allow food biogas is then converted into renewable power in the form of
or organic waste to be separated from other waste are used in electricity and heat via cogeneration or CHP with gas engines.
waste treatment sites. The residue from the digestion process is further processed into
liquid and solid fertiliser.
Food waste treatment
Biodigestion process Two common applications exist for biodigestion of food waste:
Figure 3 shows a general layout of a food waste biodigestion • On-site biodigestion. This applies to shopping malls, food
plant. production facilities, hospitals and other facilities using small
Pre-treatment is an important consideration when using food to medium sized biodigestion plants. The plant is installed at
waste anaerobic digestors. The first stage involves reduction of the site where the food waste is generated, and there is on–
the substrate to a size suitable for biodigestion. This may be site use of the gas produced. At the bottom end of the range
achieved by shredding or grinding the waste which has been are household and remote eco-lodge sized units that rely on
separated, or conversion to a pulp in the waste separation plant. food and other organic waste to produce gas which is used
Pre-treatment of the pulped waste may be applied depending mainly for cooking. At the upper end are food processing
on the process. Heat treatment has been found to increase the plants, such as wineries or fruit juice producers. Small
gas yield, and the addition of minerals and enzymes also impacts transportable modular units have been developed, making it
the process. From here it is loaded into the digestor by various possible to process food waste from shopping malls, hospitals,
means depending upon the constitution of waste materials. In the universities, military camps, holiday resorts and other sites
where food is sold or distributed in fresh or prepared form.
• Centralised food waste biodigestion at waste disposal sites
using large, mechanised plant, and sorted or mixed solid
waste. The gas is used onsite for CHP generation with
surplus power fed to the grid, or the gas may be sold via a
distribution network.
Large scale food waste biodigestion projects
Large scale centralised biodigestors tend to be more efficient
than on site units and allow more control over the digestion
process and such features as pre-treatment. Biodigestion of food
waste at waste disposal sites has been applied extensively. In the
UK in 2019 there were 94 food waste biodigestors in operation,
handling approximately 8% of British food waste, and producing
Figure 3: Food waste biodigestion plant an estimated 220 MWe of electricity. 2
energize | February 2021 | 34