Page 33 - Energize February 2021
P. 33
TECHNICAL
contacts, while also determining
timing results.
• Motion or contact travel: This
checks the operating mechanism
and mechanical linkage and
indicates potential mechanical wear.
• Coil current: The current signature
curve of the command coils during
breaker operation is recorded
during a timing test. Deviations
show possible electrical or
mechanical defects of the trip or
close control components.
According to the IEC, the trip coil
shall work between 70 and 110% of
nominal voltage and the close coil
shall work between 85% and 110 %
of nominal voltage.
• Motor current: The motor
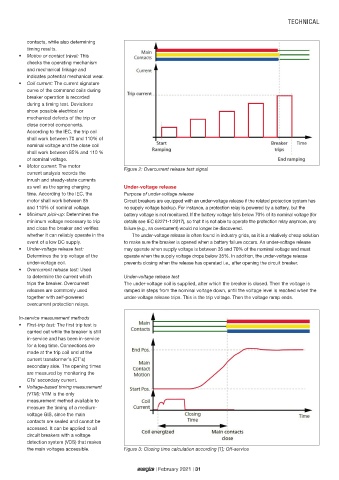
Figure 2: Overcurrent release test signal
current analysis records the
inrush and steady-state currents
as well as the spring charging Under-voltage release
time. According to the IEC, the Purpose of under-voltage release
motor shall work between 85 Circuit breakers are equipped with an under-voltage release if the related protection system has
and 110% of nominal voltage. no supply voltage backup. For instance, a protection relay is powered by a battery, but the
• Minimum pick-up: Determines the battery voltage is not monitored. If the battery voltage falls below 70% of its nominal voltage (for
minimum voltage necessary to trip details see IEC 62271-1:2017), so that it is not able to operate the protection relay anymore, any
and close the breaker and verifies failure (e.g., an overcurrent) would no longer be discovered.
whether it can reliably operate in the The under-voltage release is often found in industry grids, as it is a relatively cheap solution
event of a low DC supply. to make sure the breaker is opened when a battery failure occurs. An under-voltage release
• Under-voltage release test: may operate when supply voltage is between 35 and 70% of the nominal voltage and must
Determines the trip voltage of the operate when the supply voltage drops below 35%. In addition, the under-voltage release
under-voltage coil. prevents closing when the release has operated i.e., after opening the circuit breaker.
• Overcurrent release test: Used
to determine the current which Under-voltage release test
trips the breaker. Overcurrent The under-voltage coil is supplied, after which the breaker is closed. Then the voltage is
releases are commonly used ramped in steps from the nominal voltage down, until the voltage level is reached when the
together with self-powered under-voltage release trips. This is the trip voltage. Then the voltage ramp ends.
overcurrent protection relays.
In-service measurement methods
• First-trip test: The first trip test is
carried out while the breaker is still
in-service and has been in-service
for a long time. Connections are
made at the trip coil and at the
current transformer’s (CT’s)
secondary side. The opening times
are measured by monitoring the
CTs’ secondary current.
• Voltage-based timing measurement
(VTM): VTM is the only
measurement method available to
measure the timing of a medium-
voltage GIS, since the main
contacts are sealed and cannot be
accessed. It can be applied to all
circuit breakers with a voltage
detection system (VDS) that makes
the main voltages accessible. Figure 3: Closing time calculation according [1]; Off-service
energize | February 2021 | 31