Page 30 - Energize February 2021
P. 30
TECHNICAL
aggregates load and can calculate energy costs by business
group, department, or site. Short term load profiling is used to
provide information to control systems, while longer term can be
used for overall control of the plant energy costs.
The energy power management system can also model the
plant or process line, allowing assessment of changes before
implementation.
Controlling
After analysing the data, a control program can be developed
using several control system options. The control system should
be capable of automatic or manual operation. Programmable
automation controllers are used to provide the control
Figure 1: Industrial energy management and control system.
components of the solution. The controllers also act as data
collectors bringing discrete inputs from breakers, switches, and
the plants, on specific machines (such as refrigeration protective relays in the power management system. The
compressors) and even on individual product lines. In addition to controllers also work in concert with the personal computers
usage data, power quality information that can improve running the human machine interface.
productivity and lengthen equipment life can be gathered.
A major advantage of a power monitoring system is its ability to Control systems
capture and log real-time data and events over long periods of time. Demand management systems project future demand to assure
the peak limit is not exceeded. Load management systems can
A benefit of energy monitoring systems is the ability to more monitor the electrical consumption of selected equipment and turn
accurately allocate energy consumption and costs to specific them on and off in an operator-selected sequence to minimise
production areas or units. The system also can generate the peak demand. Loads are prioritised to allow configuration of the
reports necessary to analyse and verify utility bills and tariffs. order in which loads should be shed and restored. Load shifting
There are various ways in which monitoring can be applied: maintains a more consistent level of energy use over time, which
• Sub-metering is the deployment of power meters to monitor eases demands on utilities and avoids subsequent charges.
individual loads or work cells. A sub-metering strategy allows
measurement of differences in power consumption from shift- Energy storage
to-shift or line- to-line. This gives the ability to track the A new development in the industrial demand management field is
effectiveness of energy savings initiatives. the use of energy storage to regulate demand. The cost of storage
• Distribution system monitoring provides centralised view of the has dropped dramatically, and energy storage management
entire facility’s power distribution system, including information systems (EMS) offer a comprehensive range of features, which
for trending, alarming and targeting. Monitoring a facility’s together with an overall power/energy management system, will
power distribution system can help identify equipment allow a full range of demand management functions. Energy
approaching failure, allow reconfiguration of the electrical storage controllers offer a full range of controls over the storage
system topology, and assist with shedding loads or increasing and re-use of energy, allowing flexible decisions on when to store
local generator output. energy and when to use energy. Such decisions may be based on
• Power quality monitoring: The power quality data can be used the total demand, time-based tariffs and so on.
to pinpoint failures of motors and sensitive equipment, Load levelling involves storing power during periods of low
negotiate better service from the utility and identify the need demand on the system and delivering it during periods of high
for power factor correction and harmonic filters. The system demand, allowing reduction of peaks in demand which can vary
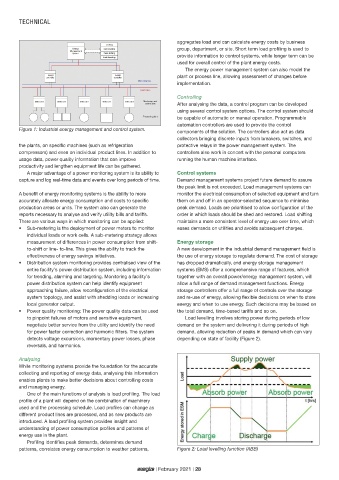
detects voltage excursions, momentary power losses, phase depending on state of facility (Figure 2).
reversals, and harmonics.
Analysing
While monitoring systems provide the foundation for the accurate
collecting and reporting of energy data, analysing this information
enables plants to make better decisions about controlling costs
and managing energy.
One of the main functions of analysis is load profiling. The load
profile of a plant will depend on the combination of machinery
used and the processing schedule. Load profiles can change as
different product lines are processed, and as new products are
introduced. A load profiling system provides insight and
understanding of power consumption profiles and patterns of
energy use in the plant.
Profiling identifies peak demands, determines demand
patterns, correlates energy consumption to weather patterns, Figure 2: Load levelling function (ABB)
energize | February 2021 | 28