Page 66 - Energize November 2021
P. 66
TECHNICAL
is therefore dependent on the voltage and
power rating of the AFE.
Whereas this phase shift is typically
in the range of 0,1° to 0,2° for a power
rating of 10 kW/400 V, phase shifts of
1° to 2° occur for 100 kW/400 V. These
phase shifts are compensated so that the
mains current is in phase with the voltage
at the input terminal of the drive. This
is common among all active rectification
topologies. 4
The pulse width modulated (PWM)
Figure 8: Active front end VFD system (ABB) waveform of the voltage from the IGBTs’
switching is smoothed by the input
additional IGBTs, the cost of an active front end drive can be more than other VFDs in inductance to closer approximate a pure
many applications. Also, the capacitive filter and the IGBTs are not as robust as the simple, sine wave.
but reliable, magnetics and diode technology of the 18-pulse drives.
Input filter (Schneider)
Operation Due to the switching actions of the
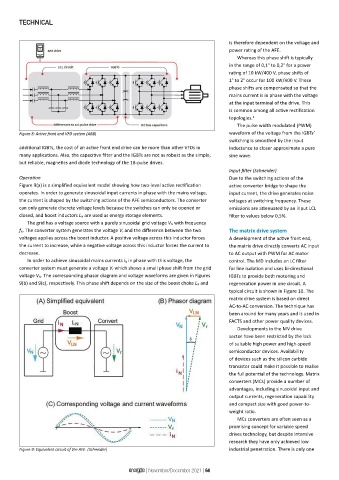
Figure 9(a) is a simplified equivalent model showing how two-level active rectification active converter bridge to shape the
operates. In order to generate sinusoidal input currents in phase with the mains voltage, input current, the drive generates noise
the current is shaped by the switching actions of the AFE semiconductors. The converter voltages at switching frequency. These
can only generate discrete voltage levels because the switches can only be opened or emissions are attenuated by an input LCL
closed, and boost inductors L N are used as energy storage elements. filter to values below 0,5%.
The grid has a voltage source with a purely sinusoidal grid voltage V N with frequency
f N. The converter system generates the voltage V r and the difference between the two The matrix drive system
voltages applies across the boost inductor. A positive voltage across this inductor forces A development of the active front end,
the current to increase, while a negative voltage across this inductor forces the current to the matrix drive directly converts AC input
decrease. to AC output with PWM for AC motor
In order to achieve sinusoidal mains currents i N in phase with this voltage, the control. The MD includes an LC filter
converter system must generate a voltage V r which shows a small phase shift from the grid for line isolation and uses bi-directional
voltage V N. The corresponding phasor diagram and voltage waveforms are given in Figures IGBTs to provide both motoring and
9(b) and 9(c), respectively. This phase shift depends on the size of the boost choke L N and regeneration power in one circuit. A
typical circuit is shown in Figure 10. The
matrix drive system is based on direct
AC-to-AC conversion. The technique has
been around for many years and is used in
FACTS and other power quality devices.
Developments in the MV drive
sector have been restricted by the lack
of suitable high power and high-speed
semiconductor devices. Availability
of devices such as the silicon carbide
transistor could make it possible to realise
the full potential of the technology. Matrix
converters (MCs) provide a number of
advantages, including sinusoidal input and
output currents, regeneration capability
and compact size with good power-to-
weight ratio.
MCs converters are often seen as a
promising concept for variable speed
drives technology, but despite intensive
research they have only achieved low
Figure 9: Equivalent circuit of the AFE. (Schneider) industrial penetration. There is only one
energize | November/December 2021 | 64