Page 67 - Energize November 2021
P. 67
TECHNICAL
Modular multilevel converters (MMC)
The standard MV drive operates with a
single output and input stage. Modular
multi- level converters consist of a
number of identical submodules, or
powercells, connected in series/parallel
configurations to provide both the
voltage and current requirements of the
drive, as well as to provide redundancy,
which allows simplification of designs
in both the input and output stages of
MV drives.
Scaling to different voltage levels and
power levels is only done by varying the
number of submodules. This allows the
same hardware with the same
mechanical construction to be used for
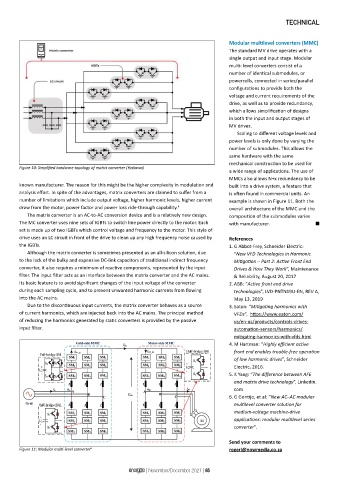
Figure 10: Simplified hardware topology of matrix converter (Yaskawa)
a wide range of applications. The use of
MMCs also allows N+x redundancy to be
known manufacturer. The reason for this might be the higher complexity in modulation and built into a drive system, a feature that
analysis effort. In spite of the advantages, matrix converters are claimed to suffer from a is often found in commercial units. An
number of limitations which include output voltage, higher harmonic levels, higher current example is shown in Figure 11. Both the
draw from the motor, power factor and power loss ride-through capability. 4 overall architecture of the MMC and the
The matrix converter is an AC-to-AC conversion device and is a relatively new design. composition of the submodules varies
The MC converter uses nine sets of IGBTs to switch line power directly to the motor. Each with manufacturer. n
set is made up of two IGBTs which control voltage and frequency to the motor. This style of
drive uses an LC circuit in front of the drive to clean up any high frequency noise caused by References
the IGBTs. 1. G Abbot-Frey, Schneider Electric:
Although the matrix converter is sometimes presented as an all-silicon solution, due “New VFD Technologies in Harmonic
to the lack of the bulky and expensive DC-link capacitors of traditional indirect frequency Mitigation – Part 2: Active Front End
converter, it also requires a minimum of reactive components, represented by the input Drives & How They Work”, Maintenance
filter. The input filter acts as an interface between the matrix converter and the AC mains. & Reliability, August 20, 2017
Its basic feature is to avoid significant changes of the input voltage of the converter 2. ABB: “Active front end drive
during each sampling cycle, and to prevent unwanted harmonic currents from flowing technologies”, LVD-PNTN19U-EN, REV A,
into the AC mains. May 13, 2019
Due to the discontinuous input currents, the matrix converter behaves as a source 3. Eaton: “Mitigating harmonics with
of current harmonics, which are injected back into the AC mains. The principal method VFDs”, https://www.eaton.com/
of reducing the harmonics generated by static converters is provided by the passive us/en-us/products/controls-drives-
input filter. automation-sensors/harmonics/
mitigating-harmonics-with-vfds.html
4. M Hartman: “Highly efficient active
front end enables trouble-free operation
of low harmonic drives”, Schneider
Electric, 2016.
5. K Yang: “The difference between AFE
and matrix drive technology”, Linkedin.
com
6. G Gontijo, et al: “New AC–AC modular
multilevel converter solution for
medium-voltage machine-drive
applications: modular multilevel series
converter”.
Send your comments to
Figure 11: Modular multi-level converter 6 rogerl@nowmedia.co.za
energize | November/December 2021 | 65