Page 61 - Energize October 2022
P. 61
TECHNICAL
either be isochronous (where voltage
and frequency stay constant at a 100%
regardless of the load) or droop (where
the voltage and frequency vary as the
load varies).
The advantage of isochronous
load sharing is the constant voltage
and frequency; however, it requires
the sources to communicate with
each other. On the other hand, droop
does not require communication
interconnection between the power
sources at the expense of varying
voltage and frequency as the load
varies. The load govern function applies
when a generator set, or multiple sets Figure 3
are paralleled to a utility or the grid.
Because the utility voltage and paralleling control and it can either be isochronous, the most common and preferred
frequency are fixed, the generator sets method or droop as described earlier.
regulate their kW and kVAR output, When it comes to load sharing with inverters, one method would be to set the
instead of their frequency and voltage. generator sets to operate as the utility (load sharing/grid forming), and the inverters
It is expected that the synchronous would operate in grid following and act like a constant real-reactive power (PQ) source.
generator onboard paralleling controls An external control system would send these PQ commands to the inverter.
have paralleling and protection
capabilities built in. Microgrid controller
At the heart of any microgrid power system there must be an autonomous controller
The generator sets’ paralleling control (Figure 4). The microgrid controller is expected to do, as a minimum, the following:
is typically responsible for all the • Optimise energy production from all energy sources to meet demand
following: • Maximise the output power of renewable sources
• Paralleling functions • Control loads via load add and load shed
• First start arbitration • Minimise emissions and fuel consumption
• Synchronising (phase angle, • Achieve the lowest levelised cost of energy (LCOE) and total cost of ownership (TCO)
voltage, frequency) for all assets
• Load sharing (kW and kVAR)
• Protection
• Metering
• Alarms
• Built-in safe manual paralleling
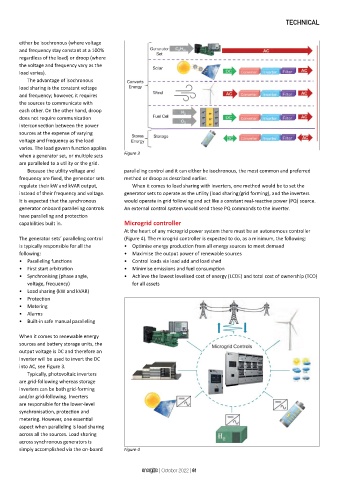
When it comes to renewable energy
sources and battery storage units, the
output voltage is DC and therefore an
inverter will be used to invert the DC
into AC, see Figure 3.
Typically, photovoltaic inverters
are grid-following whereas storage
inverters can be both grid-forming
and/or grid-following. Inverters
are responsible for the lower-level
synchronisation, protection and
metering. However, one essential
aspect when paralleling is load sharing
across all the sources. Load sharing
across synchronous generators is
simply accomplished via the on-board Figure 4
energize | October 2022 | 61