Page 52 - Energize August 2022
P. 52
TECHNICAL
Evaluation of transformer solid insulation
By I.A.R. Gray, Oilwatch Transformer Service
iquid impregnated cellulose materials Furan analysis
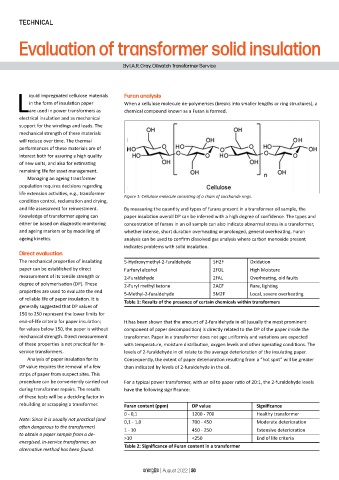
in the form of insulation paper When a cellulose molecule de-polymerises (breaks into smaller lengths or ring structures), a
Lare used in power transformers as chemical compound known as a Furan is formed.
electrical insulation and as mechanical
support for the windings and leads. The
mechanical strength of these materials
will reduce over time. The thermal
performances of these materials are of
interest both for assuring a high quality
of new units, and also for estimating
remaining life for asset management.
Managing an ageing transformer
population requires decisions regarding
life extension activities, e.g., transformer Figure 1: Cellulose molecule consisting of a chain of saccharide rings.
condition control, reclamation and drying,
and life assessment for reinvestment. By measuring the quantity and types of furans present in a transformer oil sample, the
Knowledge of transformer ageing can paper insulation overall DP can be inferred with a high degree of confidence. The types and
either be based on diagnostic monitoring concentration of furans in an oil sample can also indicate abnormal stress in a transformer,
and ageing markers or by modelling of whether intense, short duration overheating or prolonged, general overheating. Furan
ageing kinetics. analysis can be used to confirm dissolved gas analysis where carbon monoxide present
indicates problems with solid insulation.
Direct evaluation
The mechanical properties of insulating 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde 5H2F Oxidation
paper can be established by direct Furfuryl alcohol 2FOL High Moisture
measurement of its tensile strength or 2-Furaldehyde 2FAL Overheating, old faults
degree of polymerisation (DP). These 2-Furyl methyl ketone 2ACF Rare, lighting
properties are used to evaluate the end 5-Methyl-2-furaldehyde 5M2F Local, severe overheating
of reliable life of paper insulation. It is Table 1: Results of the presence of certain chemicals within transformers
generally suggested that DP values of
150 to 250 represent the lower limits for
end-of-life criteria for paper insulation; It has been shown that the amount of 2-furaldehyde in oil (usually the most prominent
for values below 150, the paper is without component of paper decomposition) is directly related to the DP of the paper inside the
mechanical strength. Direct measurement transformer. Paper in a transformer does not age uniformly and variations are expected
of these properties is not practical for in- with temperature, moisture distribution, oxygen levels and other operating conditions. The
service transformers. levels of 2-furaldehyde in oil relate to the average deterioration of the insulating paper.
Analysis of paper insulation for its Consequently, the extent of paper deterioration resulting from a “hot spot” will be greater
DP value requires the removal of a few than indicated by levels of 2-furaldehyde in the oil.
strips of paper from suspect sites. This
procedure can be conveniently carried out For a typical power transformer, with an oil to paper ratio of 20:1, the 2-furaldehyde levels
during transformer repairs. The results have the following significance:
of these tests will be a deciding factor in
rebuilding or scrapping a transformer. Furan content (ppm) DP value Significance
0 - 0,1 1200 - 700 Healthy transformer
Note: Since it is usually not practical (and 0,1 - 1,0 700 - 450 Moderate deterioration
often dangerous to the transformer) 1 - 10 450 - 250 Extensive deterioration
to obtain a paper sample from a de- >10 <250 End of life criteria
energised, in-service transformer, an
alternative method has been found. Table 2: Significance of Furan content in a transformer
energize | August 2022 | 50