Page 23 - EngineerIT November 2021
P. 23
AUTOMATION AND CONTROL
Input protection link – but the level of rejection needed is lower than that of DAQ
As the input terminals of the DAQ centralised system are often exposed centralised systems.
to external access, they are susceptible to damage from the likes of • Power and area. Low power and compact solution size are common
miswiring, signal over-ranging and ESD. Additional protection circuitry requirements for edge node systems. Low power is essential for
is often required to help protect the DAQ input. battery-powered systems. The size of the system impacts the
system housing material cost, the ease of installation and, in the
Aliasing rejection case of vibration sensing systems, the mechanical characteristics of
The vendors of systems utilising the DAQ centralised architecture the sensor.
do not always control the sensor and the input signal that is to be
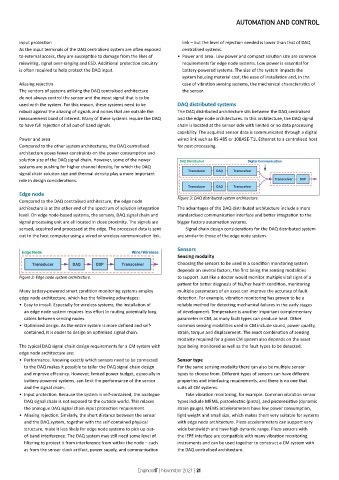
used with the system. For this reason, these systems need to be DAQ distributed systems
robust against the aliasing of signals and noises that are outside the The DAQ distributed architecture sits between the DAQ centralised
measurement band of interest. Many of these systems require the DAQ and the edge node architectures. In this architecture, the DAQ signal
to have full rejection of all out-of-band signals. chain is located at the sensor side with limited or no data processing
capability. The acquired sensor data is communicated through a digital
Power and area wired link such as RS-485 or 10BASE-T1L Ethernet to a centralised host
Compared to the other system architectures, the DAQ centralised for post-processing.
architecture poses fewer constraints on the power consumption and
solution size of the DAQ signal chain. However, some of the newer
systems are pushing for higher channel density, for which the DAQ
signal chain solution size and thermal density play a more important
role in design considerations.
Edge node
Compared to the DAQ centralised architecture, the edge node Figure 3: DAQ distributed system architecture.
architecture is at the other end of the spectrum of solution integration The advantages of the DAQ distributed architecture include a more
level. On edge node-based systems, the sensors, DAQ signal chain and standardised communication interface and better integration to the
signal processing unit are all located in close proximity. The signals are bigger factory automation systems.
sensed, acquired and processed at the edge. The processed data is sent Signal chain design considerations for the DAQ distributed system
out to the host computer using a wired or wireless communication link. are similar to those of the edge node system.
Sensors
Sensing modality
Choosing the sensors to be used in a condition monitoring system
depends on several factors, the first being the sensing modalities
Figure 2: Edge node system architecture. to support. Just like a doctor would monitor multiple vital signs of a
patient for better diagnosis of his/her health condition, monitoring
Many battery-powered smart condition monitoring systems employ multiple parameters of an asset can improve the accuracy of fault
edge node architecture, which has the following advantages: detection. For example, vibration monitoring has proven to be a
• Easy to install. Especially for wireless systems, the installation of reliable method for detecting mechanical failures in the early stages
an edge node system requires less effort in routing potentially long of development. Temperature is another important complementary
cables between sensing nodes. parameter in CM, as many fault types can produce heat. Other
• Optimised design. As the entire system is more defined and self- common sensing modalities used in CM include sound, power quality,
contained, it is easier to design an optimised signal chain. strain, torque and displacement. The exact combination of sensing
modality required for a given CM system also depends on the asset
The typical DAQ signal chain design requirements for a CM system with type being monitored as well as the fault types to be detected.
edge node architecture are:
• Performance. Knowing exactly which sensors need to be connected Sensor type
to the DAQ makes it possible to tailor the DAQ signal chain design For the same sensing modality there can also be multiple sensor
and improve efficiency. However, limited power budget, especially in types to choose from. Different types of sensors can have different
battery-powered systems, can limit the performance of the sensor properties and interfacing requirements, and there is no one that
and the signal chain. suits all CM systems.
• Input protection. Because the system is self-contained, the analogue Take vibration monitoring, for example. Common vibration sensor
DAQ signal chain is not exposed to the outside world. This relaxes types include MEMS, piezoelectric (piezo), and piezoresistive (dynamic
the analogue DAQ signal chain input protection requirement. strain gauge). MEMS accelerometers have low power consumption,
• Aliasing rejection. Similarly, the short distance between the sensor light weight and small size, which makes them very suitable for systems
and the DAQ system, together with the self-contained physical with edge node architecture. Piezo accelerometers can support very
structure, make it less likely for edge node systems to pick up out- wide bandwidth and have high dynamic range. Piezo sensors with
of-band interference. The DAQ system may still need some level of the IEPE interface are compatible with many vibration monitoring
filtering to protect it from interference from within the node – such instruments and can be used together to construct a CM system with
as from the sensor clock artifact, power supply, and communication the DAQ centralised architecture.
EngineerIT | November 2021 | 21