Page 44 - Energize July 2021
P. 44
TECHNICAL
Diesel emissions: A breath of fresh air
by Steven Lumley, WearCheck
As the world moves to adopt more planet-friendly strategies, air pollution is a key focus area for
engine-manufacturers and operators. In this article – the first of a two-part series – global diesel
engine emission standards are discussed, along with a range of techniques that reduce emissions,
which ones are most effective, and why.
t is well known that one of the main causes of climate change
is global warming, which in turn is caused by the greenhouse
Ieffect, which is caused by the atmospheric accumulation of
greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide,
ozone and water vapour.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that plays a major
role in shaping the earth’s climate, but since the Industrial Revolution
began in the latter half of the 18th century, human activities have added
more heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere. These gas emissions
have increased the greenhouse effect and caused the earth’s surface
temperature to rise.
Increased global temperatures result in glacier retreat, ocean levels
rising, changes in weather patterns and the timing of seasonal events,
like pollination and blooming of flowers and plants, which will result in
species that depend on one another becoming out of sync.
Other side effects are higher wildlife extinction rates, ocean
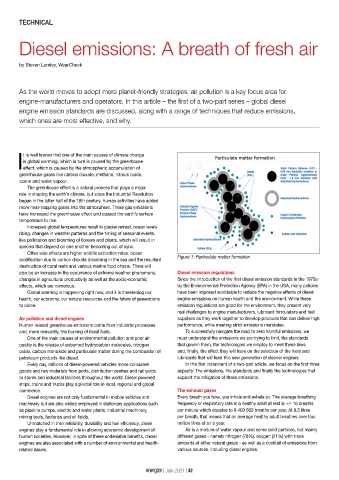
Figure 1: Particulate matter formation
acidification due to carbon dioxide dissolving in the sea and the resultant
destruction of coral reefs and various marine food chains. There will
also be an increase in the occurrence of extreme weather phenomena, Diesel emission regulations
changes in agricultural productivity as well as the socio-economic Since the introduction of the first diesel emission standards in the 1970s
effects, which are numerous. by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the USA, many policies
Global warming is happening right now, and it is threatening our have been imposed worldwide to reduce the negative effects of diesel
health, our economy, our natural resources and the future of generations engine emissions on human health and the environment. While these
to come. emission regulations are good for the environment, they present very
real challenges to engine manufacturers, lubricant formulators and fuel
Air pollution and diesel engines suppliers as they work together to develop products that can deliver high
Human-related greenhouse emissions come from industrial processes performance, while meeting strict emissions mandates.
and, more relevantly, the burning of fossil fuels. To successfully navigate the road to zero harmful emissions, we
One of the main causes of environmental pollution and poor air must understand the emissions we are trying to limit, the standards
quality is the release of unburned hydrocarbon molecules, nitrogen that govern them, the technologies we employ to meet these laws
oxide, carbon monoxide and particulate matter during the combustion of and, finally, the effect they will have on the selection of the fuels and
petroleum products like diesel. lubricants that will feed this new generation of cleaner engines.
Every day, millions of diesel-powered vehicles move consumer In this first instalment of a two-part article, we focus on the first three
goods and raw materials from ports, distribution centres and rail yards aspects: The emissions, the standards and finally the technologies that
to stores and industrial facilities throughout the world. Diesel powered support the mitigation of these emissions.
ships, trains and trucks play a pivotal role in local, regional and global
commerce. The exhaust gases
Diesel engines are not only fundamental in mobile vehicles and Every breath you take, you inhale and exhale air. The average breathing
machinery but are also widely employed in stationary applications such frequency or respiratory rate in a healthy adult at rest is +/- 16 breaths
as pipeline pumps, electric and water plants, industrial machinery, per minute which equates to 8 409 600 breaths per year. At 0,5 litres
mining tools, factories and oil fields. per breath, that means that an average healthy adult breathes over four
Unmatched in their reliability, durability and fuel efficiency, diesel million litres of air a year.
engines play a fundamental role in allowing economic development of Air is a mixture of water vapour and some solid particles, but mainly
human societies. However, in spite of these undeniable benefits, diesel different gases - namely nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%) with trace
engines are also associated with a number of environmental and health- amounts of other natural gases - as well as a cocktail of emissions from
related issues. various sources, including diesel engines.
energize | July 2021 | 42