Page 75 - Energize October 2022
P. 75
TECHNICAL
Process for battery testing
Stationary vented lead-acid cells and blocks with positive tubular plates were endurance
tested by the manufacturer
Information from BAE
tationary batteries are used in IEC 61 427:2002-04, Chapter 8.4 “Secondary cells and batteries for PV energy systems
applications where an absolutely – General requirements and methods of test”
Sreliable power supply must be • Product group: Vented lead acid cells with positive tubular plates
ensured for periods of time ranging • Type designation: 6 cells of 6 PVS 420; 1 block 12 V 3PVS 210 (6 cells)
from seconds to hours. Typical • Test laboratory: BAE’s Berlin facility in Germany
applications are systems for the • Test temperature: 20°C / 40°C
uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
in data centres, telecommunications Test carried out
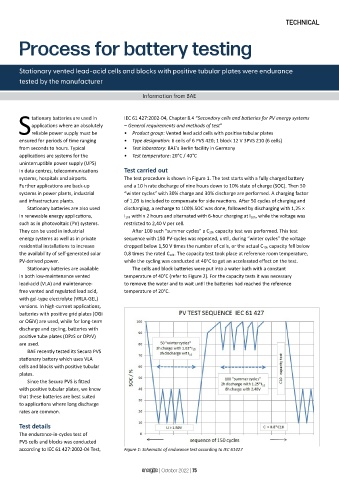
systems, hospitals and airports. The test procedure is shown in Figure 1. The test starts with a fully charged battery
Further applications are back-up and a 10 h rate discharge of nine hours down to 10% state of charge (SOC). Then 50
systems in power plants, industrial “winter cycles” with 30% charge and 30% discharge are performed. A charging factor
and infrastructure plants. of 1,03 is included to compensate for side reactions. After 50 cycles of charging and
Stationary batteries are also used discharging, a recharge to 100% SOC was done, followed by discharging with 1,25 ×
in renewable energy applications, I 10h within 2 hours and alternated with 6-hour charging at I 10h, while the voltage was
such as in photovoltaic (PV) systems. restricted to 2,40 V per cell.
They can be used in industrial After 100 such “summer cycles” a C 10h capacity test was performed. This test
energy systems as well as in private sequence with 150 PV-cycles was repeated, until, during “winter cycles” the voltage
residential installations to increase dropped below 1,50 V times the number of cells, or the actual C 10h capacity fell below
the availability of self-generated solar 0,8 times the rated C 10h. The capacity test took place at reference room temperature,
PV-derived power. while the cycling was conducted at 40°C to get an accelerated effect on the test.
Stationary batteries are available The cells and block batteries were put into a water bath with a constant
in both low-maintenance vented temperature of 40°C (refer to Figure 2). For the capacity tests it was necessary
lead-acid (VLA) and maintenance- to remove the water and to wait until the batteries had reached the reference
free vented and regulated lead acid, temperature of 20°C.
with gel-type electrolyte (VRLA-GEL)
versions. In high-current applications,
batteries with positive grid plates (OGi
or OGiV) are used, while for long-term
discharge and cycling, batteries with
positive tube plates (OPzS or OPzV)
are used.
BAE recently tested its Secura PVS
stationary battery which uses VLA
cells and blocks with positive tubular
plates.
Since the Secura PVS is fitted
with positive tubular plates, we know
that these batteries are best suited
to applications where long discharge
rates are common.
Test details
The endurance-in-cycles test of
PVS cells and blocks was conducted
according to IEC 61 427:2002-04 Test, Figure 1: Schematic of endurance test according to IEC 61427
energize | October 2022 | 75