Page 71 - Energize October 2022
P. 71
TECHNICAL
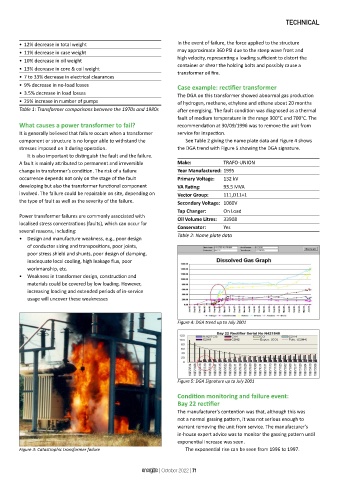
• 12% decrease in total weight In the event of failure, the force applied to the structure
• 11% decrease in case weight may approximate 360 PSI due to the steep wave front and
• 10% decrease in oil weight high velocity, representing a loading sufficient to distort the
container or shear the holding bolts and possibly cause a
• 13% decrease in core & coil weight transformer oil fire.
• 7 to 33% decrease in electrical clearances
• 9% decrease in no-load losses Case example: rectifier transformer
• 3.5% decrease in load losses The DGA on this transformer showed abnormal gas production
• 25% increase in number of pumps of hydrogen, methane, ethylene and ethane about 20 months
Table 1: Transformer comparisons between the 1970s and 1980s after energising. The fault condition was diagnosed as a thermal
fault of medium temperature in the range 300°C and 700°C. The
What causes a power transformer to fail? recommendation at 30/09/1996 was to remove the unit from
It is generally believed that failure occurs when a transformer service for inspection.
component or structure is no longer able to withstand the See Table 2 giving the name plate data and Figure 4 shows
stresses imposed on it during operation. the DGA trend with Figure 5 showing the DGA signature.
It is also important to distinguish the fault and the failure.
A fault is mainly attributed to permanent and irreversible Make: TRAFO-UNION
change in transformer’s condition. The risk of a failure Year Manufactured: 1995
occurrence depends not only on the stage of the fault Primary Voltage: 132 kV
developing but also the transformer functional component VA Rating: 93.5 MVA
involved. The failure could be repairable on site, depending on Vector Group: 111,D11+1
the type of fault as well as the severity of the failure. Secondary Voltage: 1060V
Tap Changer: On Load
Power transformer failures are commonly associated with Oil Volume Litres: 33908
localised stress concentrations (faults), which can occur for
several reasons, including: Conservator: Yes
• Design and manufacture weakness, e.g., poor design Table 2: Name plate data
of conductor sizing and transpositions, poor joints,
poor stress shield and shunts, poor design of clamping,
inadequate local cooling, high leakage flux, poor
workmanship, etc.
• Weakness in transformer design, construction and
materials could be covered by low loading. However,
increasing loading and extended periods of in-service
usage will uncover these weaknesses
Figure 4: DGA trend up to July 2001
Figure 5: DGA Signature up to July 2001
Condition monitoring and failure event:
Bay 22 rectifier
The manufacturer’s contention was that, although this was
not a normal gassing pattern, it was not serious enough to
warrant removing the unit from service. The manufacturer’s
in-house expert advice was to monitor the gassing pattern until
exponential increase was seen.
Figure 3: Catastrophic transformer failure The exponential rise can be seen from 1996 to 1997.
energize | October 2022 | 71