Page 64 - Energize April 2022
P. 64
TECHNICAL
Single units of either technology lose efficiency when
operating at partial load and also exhibit a minimum load
below which they cannot operate within allowed limits of
performance. A technical constraint for partial load operation
of gas turbine power plants is the minimum environmental
load, also called the minimum emissions-compliant load. This
is the lowest output at which the generating unit can operate
and still meet environmental limits for nitrous oxides (NOx) and
carbon monoxide (CO) emissions. The minimum environmental
load for most gas turbines is about 50% of full output because
operation at lower loads can result in potential emissions-permit
exceedances. In combined cycle plants, the gas turbine outlet
temperature must also be kept high to produce sufficient steam
to power the steam turbine.
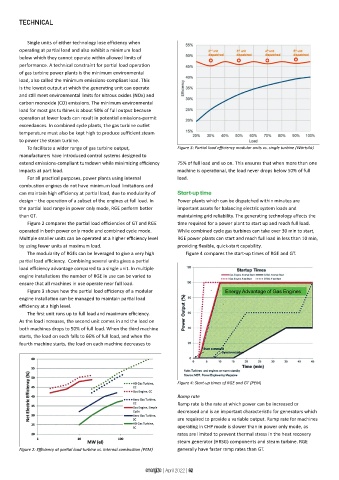
To facilitate a wider range of gas turbine output, Figure 3: Partial load efficiency modular units vs. single turbine (Wärtsilä)
manufacturers have introduced control systems designed to
extend emissions-compliant turndown while minimizing efficiency 75% of full load and so on. This ensures that when more than one
impacts at part load. machine is operational, the load never drops below 50% of full
For all practical purposes, power plants using internal load.
combustion engines do not have minimum load limitations and
can maintain high efficiency at partial load, due to modularity of Start-up time
design – the operation of a subset of the engines at full load. In Power plants which can be dispatched within minutes are
the partial load range in power only mode, RGE perform better important assets for balancing electric system loads and
than GT. maintaining grid reliability. The generating technology affects the
Figure 2 compares the partial load efficiencies of GT and RGE time required for a power plant to start up and reach full load.
operated in both power only mode and combined cycle mode. While combined cycle gas turbines can take over 30 min to start,
Multiple smaller units can be operated at a higher efficiency level RGE power plants can start and reach full load in less than 10 min,
by using fewer units at maximum load. providing flexible, quick-start capability.
The modularity of RGEs can be leveraged to give a very high Figure 4 compares the start-up times of RGE and GT.
partial load efficiency. Combining several units gives a partial
load efficiency advantage compared to a single unit. In multiple
engine installations the number of RGE in use can be varied to
ensure that all machines in use operate near full load.
Figure 3 shows how the partial load efficiency of a modular
engine installation can be managed to maintain partial load
efficiency at a high level.
The first unit runs up to full load and maximum efficiency.
As the load increases, the second unit comes in and the load on
both machines drops to 50% of full load. When the third machine
starts, the load on each falls to 66% of full load, and when the
fourth machine starts, the load on each machine decreases to
Figure 4: Start-up times of RGE and GT (PEM)
Ramp rate
Ramp rate is the rate at which power can be increased or
decreased and is an important characteristic for generators which
are required to provide a variable output. Ramp rate for machines
operating in CHP mode is slower than in power only mode, as
rates are limited to prevent thermal stress in the heat recovery
steam generator (HRSG) components and steam turbine. RGE
Figure 2: Efficiency at partial load turbine vs. internal combustion (PEM) generally have faster ramp rates than GT.
energize | April 2022 | 62