Page 65 - Energize April 2022
P. 65
TECHNICAL
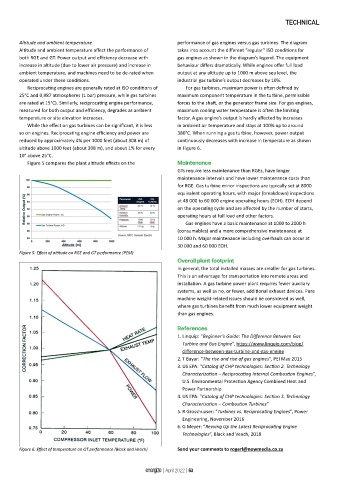
Altitude and ambient temperature performance of gas engines versus gas turbines. The diagram
Altitude and ambient temperature affect the performance of takes into account the different “regular” ISO conditions for
both RGE and GT. Power output and efficiency decrease with gas engines as shown in the diagram’s legend. The equipment
increase in altitude (due to lower air pressure) and increase in behaviour differs dramatically. While engines offer full load
ambient temperature, and machines need to be de-rated when output at any altitude up to 1000 m above sea level, the
operated under these conditions. industrial gas turbine’s output decreases by 10%.
Reciprocating engines are generally rated at ISO conditions of For gas turbines, maximum power is often defined by
25°C and 0,987 atmospheres (1 bar) pressure, while gas turbines maximum component temperature in the turbine, permissible
are rated at 15°C). Similarly, reciprocating engine performance, forces to the shaft, or the generator frame size. For gas engines,
measured for both output and efficiency, degrades as ambient maximum cooling water temperature is often the limiting
temperature or site elevation increases. factor. A gas engine’s output is hardly affected by increases
While the effect on gas turbines can be significant, it is less in ambient air temperature and stays at 100% up to around
so on engines. Reciprocating engine efficiency and power are 380°C. When running a gas turbine, however, power output
reduced by approximately 4% per 1000 feet (about 308 m) of continuously decreases with increase in temperature as shown
altitude above 1000 feet (about 308 m), and about 1% for every in Figure 6.
10° above 25°C.
Figure 5 compares the plant altitude effects on the Maintenance
GTs require less maintenance than RGEs, have longer
maintenance intervals and have lower maintenance costs than
for RGE. Gas turbine minor inspections are typically set at 8000
equivalent operating hours, with major (breakdown) inspections
at 48 000 to 60 000 engine operating hours (EOH). EOH depend
on the operating cycle and are affected by the number of starts,
operating hours at full load and other factors.
Gas engines have a basic maintenance at 1000 to 2000 h
(consumables) and a more comprehensive maintenance at
10 000 h. Major maintenance including overhauls can occur at
30 000 and 60 000 EOH.
Figure 5: Effect of altitude on RGE and GT performance (PEM)
Overall plant footprint
In general, the total installed masses are smaller for gas turbines.
This is an advantage for transportation into remote areas and
installation. A gas turbine power plant requires fewer auxiliary
systems, as well as no, or fewer, additional exhaust devices. Pure
machine weight-related issues should be considered as well,
where gas turbines benefit from much lower equipment weight
than gas engines.
References
1. Linquip: “Beginner’s Guide: The Difference Between Gas
Turbine and Gas Engine”, https://www.linquip.com/blog/
difference-between-gas-turbine-and-gas-engine
2. T Bayar: “The rise and rise of gas engines”, PEI May 2015
3. US EPA: “Catalog of CHP technologies: Section 2. Technology
Characterization – Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines”,
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Combined Heat and
Power Partnership
4. US EPA: “Catalog of CHP technologies: Section 3. Technology
Characterization – Combustion Turbines”
5. R Grosshuaser: “Turbines vs. Reciprocating Engines”, Power
Engineering, November 2016
6. G Meyer: “Revving Up the Latest Reciprocating Engine
Technologies”, Black and Veach, 2018
Figure 6: Effect of temperature on GT performance (Black and Veach) Send your comments to rogerl@nowmedia.co.za
energize | April 2022 | 63