Page 61 - Energize May 2022
P. 61
TECHNICAL
Winding resistance results are
usually interpreted based on comparing
measurements made separately on each
phase of a wye-connected winding or
between pairs of terminals on a delta-
connected winding. A comparison may
also be made with original data measured
in the factory.
A measurement is deemed
acceptable, and no further investigation
is needed, if the individual phase
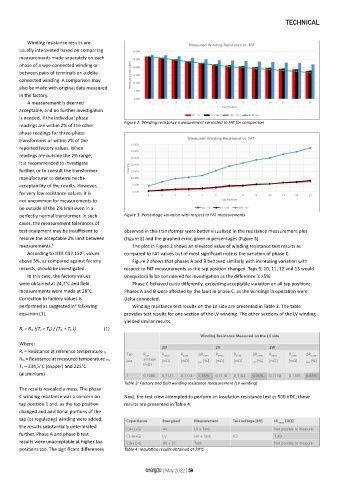
readings are within 2% of the other Figure 2: Winding resistance measurement corrected to FAT for comparison
phase readings for three-phase
transformers or within 2% of the
reported factory values. When
readings are outside the 2% range,
it is recommended to investigate
further, or to consult the transformer
manufacturer to determine the
acceptability of the results. However,
for very low resistance values, it is
not uncommon for measurements to
be outside of the 2% limit even in a
perfectly normal transformer. In such Figure 3: Percentage variation with respect to FAT measurements
cases, the measurement tolerances of
test equipment may be insufficient to observed in this transformer were better visualised in the resistance measurement plot
resolve the acceptable 2% limit between (Figure 2) and the graphed error, given in percentages (Figure 3).
measurements. 1 The plot in Figure 2 shows an elevated value of winding resistance test results as
According to IEEE C57.152 , values compared to FAT values but of most significant note is the variation of phase C.
2
above 5%, as compared against factory Figure 2 shows that phases A and B behaved similarly with increasing variation with
records, should be investigated. respect to FAT measurements as the tap position changed. Taps 9, 10, 11, 12 and 13 would
In this case, the factory values unequivocally be considered for investigation as the difference is >5%.
were obtained at 24,7°C and field Phase C behaved quite differently, exceeding acceptable variation on all tap positions.
measurements were made at 28°C. Phases A and B were affected by the fault in phase C, as the windings in operation were
Correction to factory values is Delta connected.
performed as suggested in following Winding resistance test results on the LV side are presented in Table 3. The table
2
equation (1). provides test results for one section of the LV winding. The other sections of the LV winding
yielded similar results.
R s = R m ((T s + T k) / (T m + T k )) (1)
Where:
R s = Resistance at reference temperature Ts
R m = Resistance at measured temperature Tm
T k – 234,5°C (copper) and 225°C
(aluminium)
Table 3: Factory and field winding resistance measurement (LV winding)
The results revealed a mess. The phase
C winding resistance was a concern on Next, the test crew attempted to perform an insulation resistance test at 500 VDC; these
tap position 1 and, as the tap position results are presented in Table 4.
changed and additional portions of the
tap (or regulating) winding were added,
the results substantially deteriorated
further. Phase A and phase B test
results were unacceptable at higher tap
positions too. The significant differences Table 4: Insulation results obtained at 28°C
energize | May 2022 | 59