Page 46 - Energize September 2022
P. 46
TECHNICAL
e.g., with a square wave of 20 Hz modulating a carrier of 60 Hz,
there will be a DC term, caused by the difference between the
third harmonic of the 20 Hz modulating square wave and the 60 Hz
signal. The amplitude of the DC term will be up to 1/3 * m/2.
Whilst this is perfectly correct and may be required for some
users, DC components may not be welcome in some equipment.
To solve this problem, it is currently proposed to perform real time
calculations as a user defines waveforms to identify this possibility.
Users will be warned of the possibility of DC or very low frequency
components being present if and when the currently defined
signal is applied to the UUT.
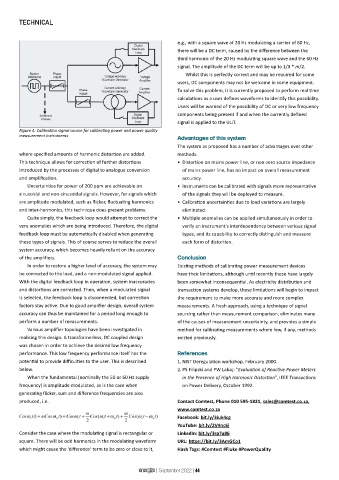
Figure 4: Calibration signal source for calibrating power and power quality
measurement instruments Advantages of this system
The system as proposed has a number of advantages over other
where specified amounts of harmonic distortion are added. methods.
This technique allows for correction of further distortions • Distortion on mains power line, or non-zero source impedance
introduced by the processes of digital to analogue conversion of mains power line, has no impact on overall measurement
and amplification. accuracy.
Uncertainties for power of 200 ppm are achievable on • Instruments can be calibrated with signals more representative
sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal signals. However, for signals which of the signals they will be deployed to measure.
are amplitude modulated, such as flicker, fluctuating harmonics • Calibration uncertainties due to load variations are largely
and inter-harmonics, this technique does present problems. eliminated.
Quite simply, the feedback loop would attempt to correct the • Multiple anomalies can be applied simultaneously in order to
very anomalies which are being introduced. Therefore, the digital verify an instrument’s interdependency between various signal
feedback loop must be automatically disabled when generating types, and its capability to correctly distinguish and measure
these types of signals. This of course serves to reduce the overall each form of distortion.
system accuracy, which becomes heavily reliant on the accuracy
of the amplifiers. Conclusion
In order to restore a higher level of accuracy, the system may Existing methods of calibrating power measurement devices
be connected to the load, and a non-modulated signal applied. have their limitations, although until recently these have largely
With the digital feedback loop in operation, system inaccuracies been somewhat inconsequential. As electricity distribution and
and distortions are corrected. Then, when a modulated signal transaction systems develop, these limitations will begin to impact
is selected, the feedback loop is disconnected, but correction the requirement to make more accurate and more complex
factors stay active. Due to good amplifier design, overall system measurements. A fresh approach, using a technique of signal
accuracy can thus be maintained for a period long enough to sourcing rather than measurement comparison, eliminates many
perform a number of measurements. of the causes of measurement uncertainty, and provides a simple
Various amplifier topologies have been investigated in method for calibrating measurements where few, if any, methods
realising this design. A transformerless, DC coupled design existed previously.
was chosen in order to achieve the desired low frequency
performance. This low frequency performance itself has the References
potential to provide difficulties to the user. This is described 1. NIST Deregulation workshop, February 2000.
below. 2. PS Filipski and PW Labaj: “Evaluation of Reactive Power Meters
When the fundamental (nominally the 50 or 60 Hz supply in the Presence of High Harmonic Distortion”, IEEE Transactions
frequency) is amplitude modulated, as is the case when on Power Delivery, October 1992.
generating flicker, sum and difference frequencies are also
produced, i.e. Contact Comtest, Phone 010 595-1821, sales@comtest.co.za,
www.comtest.co.za
Facebook: bit.ly/3iuk4cg
YouTube: bit.ly/2V4nc6j
Consider the case where the modulating signal is rectangular or LinkedIn: bit.ly/3rpTu86
square. There will be odd harmonics in the modulating waveform URL: https://bit.ly/3AmGCo1
which might cause the ‘difference’ term to be zero or close to it, Hash Tags: #Comtest #Fluke #PowerQuality
energize | September 2022 | 44