Page 50 - Energize September 2022
P. 50
TECHNICAL
PF and non-linear electric loads (and higher divisible by three) add instead of cancelling out. In
In non-linear loads the current does not have a sinusoidal balanced three-phase systems this can result in a higher-than-
waveshape but is in the form of a non- linear or distorted wave, as expected current flowing in the neutral conductor.
shown in Figure 2.
Distortion PF
Distortion PF is a measure of how much the harmonic distortion of
a load current decreases the average power transferred to the load.
The PF component due to harmonics is more difficult to analyse,
but has the same effect as displacement PF, i.e., the real power
delivered is less than the apparent power.
The problem here arises with determining the apparent power,
which is not so simple, as the current wave is not a pure sinewave.
Figure 2: Distorted waveform (Monolithic power) Real power can be calculated by integrating the products of
current and voltage over the period when current is flowing, but
Distorted and non-linear waveforms do not lend themselves to calculating apparent power is a very complicated process, and the
direct mathematical modelling in the way that sinewaves do, and conventional way of defining distortion PF makes use of the total
require special techniques to analyse the effects. Fortunately, most harmonic distortion (THD), defined as the sum of all the RMS (root-
distorted waveforms can be approximated by using a technique of mean-square) harmonic currents flowing in the network.
Fourier analysis, which provides a model consisting of an infinite Analysis of distorted waveforms shows that harmonic currents
series of waveforms at multiples of the basic frequency, and of do not contribute to the power delivered to the load but add to
different amplitudes, known as harmonics. Analysis is applied to the total current flowing in the circuit , so that the real power in
1
each individual harmonic and totaling the results gives the overall the load is that due to the fundamental component of the current
effect. waveform only.
This approach enables the design and application of filters
to reduce the effect of the distorted waveform, by using suitably The distortion PF is calculated as:
sized filters for each harmonic. Harmonics are most prevalent in
current waveforms, although voltage harmonic distortion does PFdist = = (4)
occur. It should be noted that the model is an approximation as the
waveform itself is complex, and Fourier analysis wave shapes which Where I 1 is the current of the fundamental.
can be described mathematically.
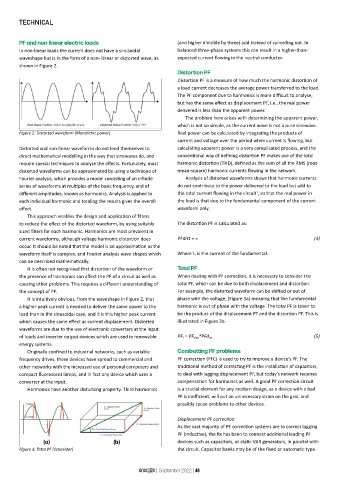
It is often not recognised that distortion of the waveform or Total PF
the presence of harmonics can affect the PF of a circuit as well as When dealing with PF correction, it is necessary to consider the
causing other problems. This requires a different understanding of total PF, which can be due to both displacement and distortion.
the concept of PF. For example, the distorted waveform can be shifted or out of
It is intuitively obvious, from the waveshape in Figure 2, that phase with the voltage, (Figure 3a) meaning that the fundamental
a higher peak current is needed to deliver the same power to the harmonic is out of phase with the voltage. The total PF is taken to
load than in the sinusoidal case, and it is this higher peak current be the product of the displacement PF and the distortion PF. This is
which causes the same effect as current displacement. Distorted illustrated in Figure 3b.
waveforms are due to the use of electronic converters at the input
of loads and inverter output devices which are used in renewable PF t = PF disp*PFd ist (5)
energy systems.
Originally confined to industrial networks, such as variable Combatting PF problems
frequency drives, these devices have spread to commercial and PF correction (PFC) is used to try to improve a device’s PF. The
other networks with the increased use of personal computers and traditional method of correcting PF is the installation of capacitors,
compact fluorescent lamps, and in fact any device which uses a to deal with lagging displacement PF, but today’s network requires
converter at the input. compensation for harmonics as well. A good PF correction circuit
Harmonics have another disturbing property. Third harmonics is a crucial element for any modern design, as a device with a bad
PF is inefficient, will put an unnecessary strain on the grid, and
possibly cause problems to other devices.
Displacement PF correction
As the vast majority of PF correction systems are to correct lagging
PF (inductive), the fix has been to connect additional leading PF
(a) (b) devices such as capacitors, or static VAR generators, in parallel with
Figure 3: Total PF (Schneider) the circuit. Capacitor banks may be of the fixed or automatic type.
energize | September 2022 | 48