Page 52 - Energize September 2022
P. 52
TECHNICAL
(a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 7: Active harmonic filter (Puresine)
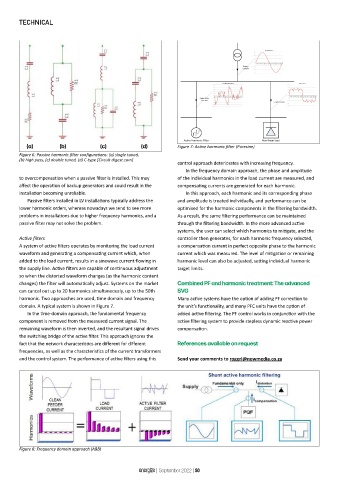
Figure 6: Passive harmonic filter configurations: (a) single tuned,
(b) high pass, (c) double tuned, (d) C-type [Circuit digest.com]
control approach deteriorates with increasing frequency.
In the frequency domain approach, the phase and amplitude
to overcompensation when a passive filter is installed. This may of the individual harmonics in the load current are measured, and
affect the operation of backup generators and could result in the compensating currents are generated for each harmonic.
installation becoming unreliable. In this approach, each harmonic and its corresponding phase
Passive filters installed in LV installations typically address the and amplitude is treated individually, and performance can be
lower harmonic orders, whereas nowadays we tend to see more optimised for the harmonic components in the filtering bandwidth.
problems in installations due to higher frequency harmonics, and a As a result, the same filtering performance can be maintained
passive filter may not solve the problem. through the filtering bandwidth. In the more advanced active
systems, the user can select which harmonics to mitigate, and the
Active filters controller then generates, for each harmonic frequency selected,
A system of active filters operates by monitoring the load current a compensation current in perfect opposite phase to the harmonic
waveform and generating a compensating current which, when current which was measured. The level of mitigation or remaining
added to the load current, results in a sinewave current flowing in harmonic level can also be adjusted, setting individual harmonic
the supply line. Active filters are capable of continuous adjustment target limits.
so when the distorted waveform changes (as the harmonic content
changes) the filter will automatically adjust. Systems on the market Combined PF and harmonic treatment: The advanced
can cancel out up to 20 harmonics simultaneously, up to the 50th SVG
harmonic. Two approaches are used, time domain and frequency Many active systems have the option of adding PF correction to
domain. A typical system is shown in Figure 7. the unit’s functionality, and many PFC units have the option of
In the time-domain approach, the fundamental frequency added active filtering. The PF control works in conjunction with the
component is removed from the measured current signal. The active filtering system to provide stepless dynamic reactive power
remaining waveform is then inverted, and the resultant signal drives compensation.
the switching bridge of the active filter. This approach ignores the
fact that the network characteristics are different for different References available on request
frequencies, as well as the characteristics of the current transformers
and the control system. The performance of active filters using this Send your comments to rogerl@nowmedia.co.za
Figure 8: Frequency domain approach (ABB)
energize | September 2022 | 50