Page 54 - Energize September 2022
P. 54
TECHNICAL
Reverse power flow
PV systems connected to the DF at multiple system points, causes
power to flow in a different direction than what the power grid
was originally designed for. This change in power flow is termed
“reverse power flow” (RPF) and can have a large, negative
impact on installed transformers, as well as other network items.
RPF requires the evaluation of existing transformer assets and
distribution infrastructure. Large additional transformer upgrades/
de-rating or replacement costs may need to be considered as well
as new distribution system investment.
Transformers are designed for step down operation (i.e.,
power flow in one direction) and operation in RPF mode can
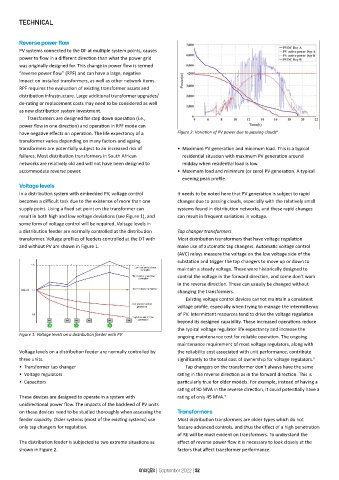
have negative effects on operation. The life expectancy of a Figure 2: Variation of PV power due to passing clouds 6
transformer varies depending on many factors and ageing
transformers are potentially subject to an increased risk of • Maximum PV generation and minimum load. This is a typical
failures. Most distribution transformers in South African residential situation with maximum PV generation around
networks are relatively old and will not have been designed to midday when residential load is low.
accommodate reverse power. • Maximum load and minimum (or zero) PV generation. A typical
evening peak profile.
Voltage levels
In a distribution system with embedded PV, voltage control It needs to be noted here that PV generation is subject to rapid
becomes a difficult task due to the existence of more than one changes due to passing clouds, especially with the relatively small
supply point. Using a fixed set point on the transformer can systems found in distribution networks, and these rapid changes
result in both high and low voltage deviations (see Figure 1), and can result in frequent variations in voltage.
some form of voltage control will be required. Voltage levels in
a distribution feeder are normally controlled at the distribution Tap changer transformers
transformer. Voltage profiles of feeders controlled at the DT with Most distribution transformers that have voltage regulation
and without PV are shown in Figure 1. make use of automatic tap changers. Automatic voltage control
(AVC) relays measure the voltage on the low voltage side of the
substation and trigger the tap changers to move up or down to
maintain a steady voltage. These were historically designed to
control the voltage in the forward direction, and some don’t work
in the reverse direction. These can usually be changed without
changing the transformers.
Existing voltage control devices cannot maintain a consistent
voltage profile, especially when trying to manage the intermittency
of PV. Intermittent resources tend to drive the voltage regulation
beyond its designed capability. These increased operations reduce
the typical voltage regulator life expectancy and increase the
Figure 1: Voltage levels on a distribution feeder with PV ongoing maintenance cost for reliable operation. The ongoing
maintenance requirement of most voltage regulators, along with
Voltage levels on a distribution feeder are normally controlled by the reliability cost associated with unit performance, contribute
three units. significantly to the total cost of ownership for voltage regulators. 3
• Transformer tap changer Tap changers on the transformer don’t always have the same
• Voltage regulators rating in the reverse direction as in the forward direction. This is
• Capacitors particularly true for older models. For example, instead of having a
rating of 90 MVA in the reverse direction, it could potentially have a
These devices are designed to operate in a system with rating of only 45 MVA. 3
unidirectional power flow. The impacts of the backfeed of PV units
on these devices need to be studied thoroughly when assessing the Transformers
feeder capacity. Older systems (most of the existing systems) use Most distribution transformers are older types which do not
only tap changers for regulation. feature advanced controls, and thus the effect of a high penetration
of RE will be most evident on transformers. To understand the
The distribution feeder is subjected to two extreme situations as effect of reverse power flow it is necessary to look closely at the
shown in Figure 2. factors that affect transformer performance.
energize | September 2022 | 52