Page 19 - EngineerIt April 2021
P. 19
ELECTRONICS
How to choose the right protection
for your circuit
Diarmúid Carey, Applications Engineer, Analog Devices
Diarmúid Carey is an applications engineer based in Ireland. He has worked as an applications engineer since 2008 and joined Analog Devices in 2017.
He holds a Bachelor of Engineering in computer engineering from the University of Limerick. He can be reached at diarmuid.carey@analog.com
Introduction surge protection circuitry include any application that requires
The increase in the amount of electronics used in all industries, high voltage or high current supplies, or those that feature supply
and the expansion of functions handled by expensive FPGAs and connections that are hot plugged, or systems that have motors
processors, has elevated the need to protect these devices from or that may be exposed to potential lightning induced transients.
the harsh environments in which they operate. Layer on top of this High voltage events can occur over a wide range of time bases,
a need for small form factors, high reliability, and fast response to from micro-seconds to hundreds of milliseconds, so a flexible
overvoltage and overcurrent surge events. and reliable protection mechanism is imperative to ensure the
longevity of costly downstream electronic devices.
Why consider voltage and current protection For instance, automotive load dump can occur when the
devices? alternator (charging the battery) is momentarily disconnected from
Automotive, industrial, communications and aviation electronic the battery. As a result of this disconnect, the full charge current
systems must operate through a range of power supply from the alternator is placed on the power rail, which raises the rail
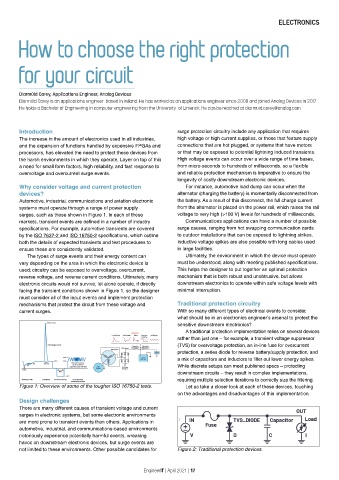
surges, such as those shown in Figure 1. In each of these voltage to very high (>100 V) levels for hundreds of milliseconds.
markets, transient events are defined in a number of industry Communications applications can have a number of possible
specifications. For example, automotive transients are covered surge causes, ranging from hot swapping communication cards
by the ISO 7637-2 and ISO 16750-2 specifications, which outline to outdoor installations that can be exposed to lightning strikes.
both the details of expected transients and test procedures to Inductive voltage spikes are also possible with long cables used
ensure these are consistently validated. in large facilities.
The types of surge events and their energy content can Ultimately, the environment in which the device must operate
vary depending on the area in which the electronic device is must be understood, along with meeting published specifications.
used; circuitry can be exposed to overvoltage, overcurrent, This helps the designer to put together an optimal protection
reverse voltage, and reverse current conditions. Ultimately, many mechanism that is both robust and unobtrusive, but allows
electronic circuits would not survive, let alone operate, if directly downstream electronics to operate within safe voltage levels with
facing the transient conditions shown in Figure 1, so the designer minimal interruption.
must consider all of the input events and implement protection
mechanisms that protect the circuit from these voltage and Traditional protection circuitry
current surges. With so many different types of electrical events to consider,
what should be in an electronics engineer’s arsenal to protect the
sensitive downstream electronics?
A traditional protection implementation relies on several devices
rather than just one — for example, a transient voltage suppressor
(TVS) for overvoltage protection, an in-line fuse for overcurrent
protection, a series diode for reverse battery/supply protection, and
a mix of capacitors and inductors to filter out lower energy spikes.
While discrete setups can meet published specs — protecting
downstream circuits — they result in complex implementations,
requiring multiple selection iterations to correctly size the filtering.
Figure 1: Overview of some of the tougher ISO 16750-2 tests. Let us take a closer look at each of these devices, touching
on the advantages and disadvantages of this implementation.
Design challenges
There are many different causes of transient voltage and current
surges in electronic systems, but some electronic environments
are more prone to transient events than others. Applications in
automotive, industrial, and communications-based environments
notoriously experience potentially harmful events, wreaking
havoc on downstream electronic devices, but surge events are
not limited to these environments. Other possible candidates for Figure 2: Traditional protection devices.
EngineerIT | April 2021 | 17