Page 22 - EngineerIT March 2022
P. 22
MEASUREMENT
How to design a good vibration sensor
enclosure using modal analysis
By Richard Anslow, System Applications Engineer, Automation and Energy Business Unit at Analog Devices
In the article
A well-constructed mechanical enclosure design for a MEMS
accelerometer will ensure that high quality vibration data for
CbM is extracted from the monitored asset. The mechanical
enclosure used to house a MEMS accelerometer needs to have
a frequency response better than the integrated MEMS. This
article uses modal analysis to provide the natural frequencies
possible with enclosure designs. Guidance on vibration sensor
design is provided using theoretical and ANSYS modal simulation
examples. It is shown that geometry effects, such as enclosure
shape (such as a cylinder or a rectangle) and height dominate
the natural frequencies in enclosure design. Mechanical design
examples are provided for housing single-axis and tri-axial MEMS
accelerometers with 21 kHz resonant frequency. This article also
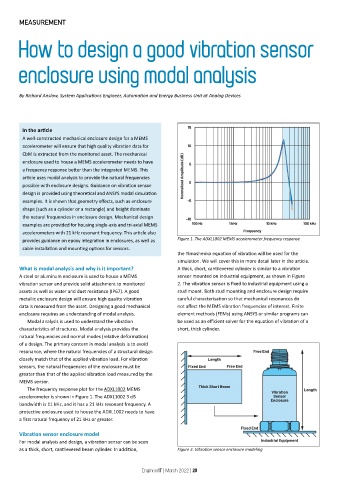
provides guidance on epoxy integration in enclosures, as well as Figure 1. The ADXL1002 MEMS accelerometer frequency response
cable installation and mounting options for sensors.
the Timoshenko equation of vibration will be used for the
simulation. We will cover this in more detail later in the article.
What is modal analysis and why is it important? A thick, short, cantilevered cylinder is similar to a vibration
A steel or aluminum enclosure is used to house a MEMS sensor mounted on industrial equipment, as shown in Figure
vibration sensor and provide solid attachment to monitored 2. The vibration sensor is fixed to industrial equipment using a
assets as well as water and dust resistance (IP67). A good stud mount. Both stud mounting and enclosure design require
metallic enclosure design will ensure high quality vibration careful characterisation so that mechanical resonances do
data is measured from the asset. Designing a good mechanical not affect the MEMS vibration frequencies of interest. Finite
enclosure requires an understanding of modal analysis. element methods (FEMs) using ANSYS or similar programs can
Modal analysis is used to understand the vibration be used as an efficient solver for the equation of vibration of a
characteristics of structures. Modal analysis provides the short, thick cylinder.
natural frequencies and normal modes (relative deformation)
of a design. The primary concern in modal analysis is to avoid
resonance, where the natural frequencies of a structural design
closely match that of the applied vibration load. For vibration
sensors, the natural frequencies of the enclosure must be
greater than that of the applied vibration load measured by the
MEMS sensor.
The frequency response plot for the ADXL1002 MEMS
accelerometer is shown in Figure 1. The ADXL1002 3 dB
bandwidth is 11 kHz, and it has a 21 kHz resonant frequency. A
protective enclosure used to house the ADXL1002 needs to have
a first natural frequency of 21 kHz or greater.
Vibration sensor enclosure model
For modal analysis and design, a vibration sensor can be seen
as a thick, short, cantilevered beam cylinder. In addition, Figure 2. Vibration sensor enclosure modeling
EngineerIT | March 2022 | 20