Page 56 - Energize November 2021
P. 56
TECHNICAL
Bubbling fluidised bed combustion
(BFBC)
Fluidised bed combustion takes place when
the forced draught fan supplies air to the
furnace of the boiler. In the furnace, sand
(used to create the bubbling phenomenon)
is placed on the bed and is heated before
fluidisation, and the air enters the bed
from the nozzles fitted on the furnace bed.
The sand opposes the upward motion of
the air above the nozzles, but at sufficient
velocities, when the pressure applied by the
air becomes equal to the weight of the sand,
fluidisation of the sand occurs. Fuel supplied
by a conveyor is fed to the preheated
bubbling sand and gets combusted. This
also ensures complete combustion of the
fuel. The heat released during combustion
heats up the surrounding boiler tubes and
generates steam. The burning fuel does not
rise above the surface of the bed.
Figure 3: Example of a bubbling fluidised bed combustor (Babcock and Wilcox)
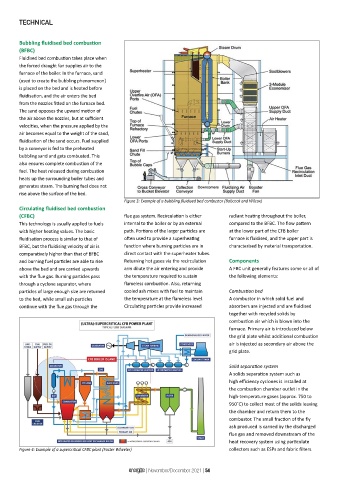
Circulating fluidised bed combustion
(CFBC) flue gas system. Recirculation is either radiant heating throughout the boiler,
This technology is usually applied to fuels internal to the boiler or by an external compared to the BFBC. The flow pattern
with higher heating values. The basic path. Portions of the larger particles are at the lower part of the CFB boiler
fluidisation process is similar to that of often used to provide a superheating furnace is fluidised, and the upper part is
BFBC, but the fluidising velocity of air is function where burning particles are in characterised by material transportation.
comparatively higher than that of BFBC direct contact with the superheater tubes.
and burning fuel particles are able to rise Returning hot gases via the recirculation Components
above the bed and are carried upwards arm dilute the air entering and provide A FBC unit generally features some or all of
with the flue gas. Burning particles pass the temperature required to sustain the following elements:
through a cyclone separator, where flameless combustion. Also, returning
particles of large enough size are returned cooled ash mixes with fuel to maintain Combustion bed
to the bed, while small ash particles the temperature at the flameless level. A combustor in which solid fuel and
continue with the flue gas through the Circulating particles provide increased absorbers are injected and are fluidised
together with recycled solids by
combustion air which is blown into the
furnace. Primary air is introduced below
the grid plate whilst additional combustion
air is injected as secondary air above the
grid plate.
Solid separation system
A solids separation system such as
high efficiency cyclones is installed at
the combustion chamber outlet in the
high-temperature gases (approx. 750 to
950˚C) to collect most of the solids leaving
the chamber and return them to the
combustor. The small fraction of the fly
ash produced is carried by the discharged
flue gas and removed downstream of the
heat recovery system using particulate
Figure 4: Example of a supercritical CFBC plant (Foster Wheeler) collectors such as ESPs and fabric filters.
energize | November/December 2021 | 54