Page 54 - Energize November 2021
P. 54
TECHNICAL
Fluidised bed boilers offer a wide range
of power generation options
by Mike Rycroft, Now Media
Solid fuel thermal power systems will still be in use for many years to come, and there will still
be new power stations built and operated. The trend however is towards high efficiency low
emission (HELE) systems which can co-fire mixtures of coal and other fuels, as well as other fuels
entirely, which will reduce carbon dioxide emissions. In this field the fluidised bed boiler has
emerged as a leader.
nterest in circulating fluidised bed an added facility, to large supercritical and Simpler design
(CFBC) boilers as a power generation ultra-supercritical plant in the order of 600 The CFBC does not use coal mills or fans,
Itechnology is increasing because MWe designed for power generation, the and the heat transfer characteristics allow
of several advantages this technology FBC has grown and developed to cover a simpler tube wall designs, with further
offers over conventional boilers, such wide range of applications and fuel types. savings from the gravity feed system used
as increased gas-solid mixing resulting for fuel and additives.
in higher combustion efficiency and Advantages of FBC
the ability to use lower quality fuels, Lower operating temperature Fuel flexibility
as well as a mixture of different fuels. The combustion temperature in a CFBC CFBs have been developed which can burn
CFBC combustors are operated at lower boiler (800 to 900˚C) is significantly lower a variety of fuels, from high- and low-
temperatures than conventional thermal than in a PCC boiler (1300 to 1700˚C), quality coal, mixtures of coal and other
power generation combustors, thus which results in considerably reduced NOx solid fuels, to biomass and waste or refuse
reducing NOx emissions. SO 2 emissions formation compared to PCC. derived fuels entirely. CFBC are especially
are conveniently controlled through suited to burning discard and other low-
the addition of calcium -based sulphur Smaller boiler size for equivalent power grade coal. The thermal stability of the bed
sorbents within the combustor. output ensures that the combustor is insensitive
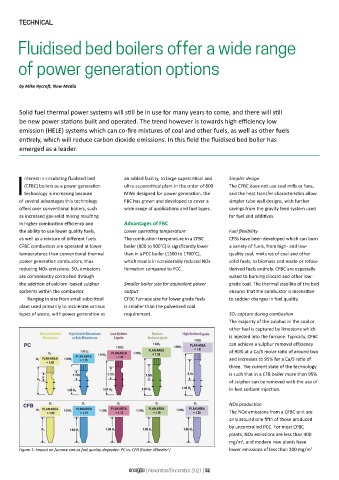
Ranging in size from small subcritical CFBC furnace size for lower grade fuels to sudden changes in fuel quality.
plant used primarily to incinerate various is smaller than the pulverised coal
types of waste, with power generation as requirement. SO 2 capture during combustion
The majority of the sulphur in the coal or
other fuel is captured by limestone which
is injected into the furnace. Typically, CFBC
can achieve a sulphur removal efficiency
of 90% at a Ca/S molar ratio of around two
and increases to 95% for a Ca/S ratio of
three. The current state of the technology
is such that in a CFB boiler more than 95%
of sulphur can be removed with the use of
in-bed sorbent injection.
NOx production
The NOx emissions from a CFBC unit are
only around one fifth of those produced
by uncontrolled PCC. For most CFBC
plants, NOx emissions are less than 400
mg/m , and modern new plants have
3
Figure 1: Impact on furnace size as fuel quality degrades: PC vs. CFB (Foster Wheeler ) lower emissions of less than 200 mg/m 3
5
energize | November/December 2021 | 52