Page 47 - Energize February 2022
P. 47
TECHNICAL
Dynamic rotary UPS systems
While static inverter-based UPS systems suffice for smaller
individual loads, for large UPS applications, in the MW range,
dynamic UPS systems based on rotating machinery are more
suitable. For large centralised UPS power the dynamic UPS meets
all the requirements for industrial use. The dynamic UPS consists
of a combination of motor/generator, coupled to an IC engine, as
shown in Figure 5.
Early models used a flywheel to store kinetic energy, but
modern designs use concentric rotating mass cylinders for this
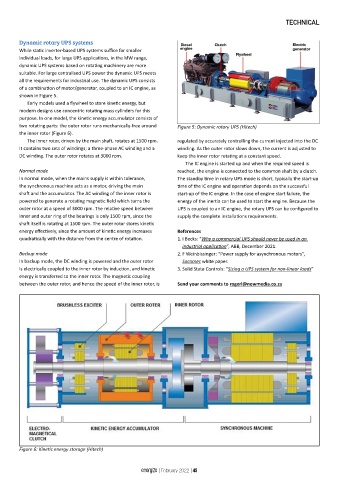
purpose. In one model, the kinetic energy accumulator consists of
two rotating parts: the outer rotor runs mechanically-free around Figure 5: Dynamic rotary UPS (Hitech)
the inner rotor (Figure 6).
The inner rotor, driven by the main shaft, rotates at 1500 rpm. regulated by accurately controlling the current injected into the DC
It contains two sets of windings; a three-phase AC winding and a winding. As the outer rotor slows down, the current is adjusted to
DC winding. The outer rotor rotates at 3000 rpm. keep the inner rotor rotating at a constant speed.
The IC engine is started up and when the required speed is
Normal mode reached, the engine is connected to the common shaft by a clutch.
In normal mode, when the mains supply is within tolerance, The standby time in rotary UPS mode is short, typically the start-up
the synchronous machine acts as a motor, driving the main time of the IC engine and operation depends on the successful
shaft and the accumulator. The AC winding of the inner rotor is start-up of the IC engine. In the case of engine start failure, the
powered to generate a rotating magnetic field which turns the energy of the inertia can be used to start the engine. Because the
outer rotor at a speed of 3000 rpm. The relative speed between UPS is coupled to an IC engine, the rotary UPS can be configured to
inner and outer ring of the bearings is only 1500 rpm, since the supply the complete installations requirements.
shaft itself is rotating at 1500 rpm. The outer rotor stores kinetic
energy effectively, since the amount of kinetic energy increases References
quadratically with the distance from the centre of rotation. 1. I Becks: “Why a commercial UPS should never be used in an
industrial application”, ABB, December 2021.
Backup mode 2. F Weinbissinger: “Power supply for asynchronous motors”,
In backup mode, the DC winding is powered and the outer rotor Socomec white paper.
is electrically coupled to the inner rotor by induction, and kinetic 3. Solid State Controls: “Sizing a UPS system for non-linear loads”
energy is transferred to the inner rotor. The magnetic coupling
between the outer rotor, and hence the speed of the inner rotor, is Send your comments to rogerl@nowmedia.co.za
Figure 6: Kinetic energy storage (Hitech)
energize | February 2022 | 45