Page 54 - Energize March 2022
P. 54
TECHNICAL
Country and region End user Agro-ecological zone Agrivoltaic system
Kenya (Kajaido county) Latia Resource Centre, agribusiness for Semi-arid 56 kWp with rainwater harvesting
farmer capacity building
Uganda ( Lamwo district) Three neighbouring villages Humid 3 x 60 kWp
Tanzania ( Morogoro) Sustainable Agriculture Tanzania, Semi-arid 35 kWp with rainwater harvesting and
non-profit agricultural training centre battery storage
Table 1: The locations, hosts, agro-ecological zones, capacities, and additional features of the three pilot agrivoltaic systems being deployed in Kenya,
Uganda and Tanzania 3
a substantial growth in off-grid households and mini-grid solar References
developments. 1. E Adeh, et al: “Solar PV power potential is greatest over
Although this high solar radiation offers extensive electricity croplands”, Nature: Scientific reports, August 2019.
generation opportunities, the associated heat and high evaporation 2. C Toledo and A Scognamiglio: “Agrivoltaic Systems Design and
also contribute to challenging conditions for crop growth, Assessment: A Critical Review, and a Descriptive Model towards
particularly in terms of water stress. With 75% of the population a Sustainable Landscape Vision (Three-Dimensional Agrivoltaic
dependent on rainfed agriculture, water shortage is a hardship Patterns)”, Sustainability 2021.
for many farmers. While the total amount of precipitation is not 3. Microgrid news: “Agrivoltaics,” a win-win strategy combining
forecast to change significantly with climate change for most of the solar and agriculture”, Microgrid news, 21 January 2020.
region, it is forecast to become more erratic and less predictable, 4. R Randle Bogis, et al: “Agrivoltaics in East Africa: Opportunities
leading to lower yields for major crops (e.g., 8 to 45% reductions in and Challenges”, AIP Conference Proceedings 2021.
yield by 2050). 3 5. E Bellini: “Special solar panels for agrivoltaics”, PV magazine,
Three pilot systems, currently under development by a team July 2020
comprising local universities and international organisations , will 5. G Roccaforte: “Eclipse: A New Photovoltaic Panel Designed for
3
test the impacts of AGV structures on crop yields and financial Greenhouses and Croplands”, AIP Conference Proceedings, 2021
added value for farmers. Each system has a different design to
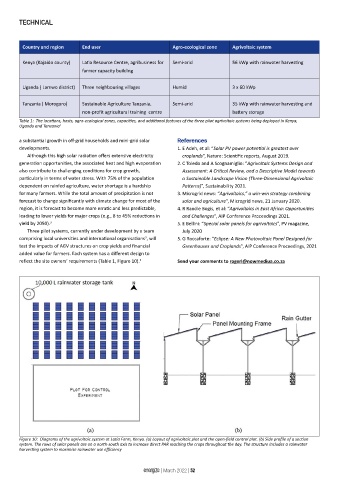
reflect the site owners’ requirements (Table 1, Figure 10). 3 Send your comments to rogerl@nowmediua.co.za
Figure 10: Diagrams of the agrivoltaic system at Latia Farm, Kenya. (a) Layout of agrivoltaic plot and the open-field control plot. (b) Side profile of a section
system. The rows of solar panels are on a north-south axis to increase direct PAR reaching the crops throughout the day. The structure includes a rainwater
harvesting system to maximise rainwater use efficiency
energize | March 2022 | 52