Page 16 - EngineerIT April 2022
P. 16
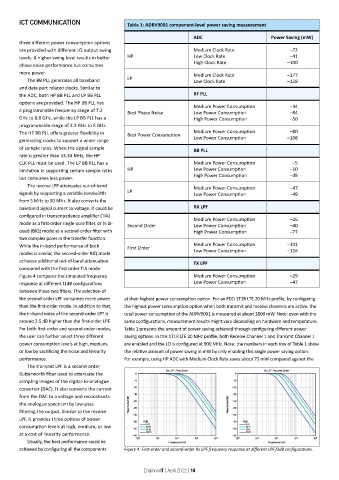
ICT COMMUNICATION Table 1: ADRV9001 component-level power saving measurement
ADC Power Saving (mW)
three different power consumption options
are provided with different LO output swing Medium Clock Rate –72
levels. A higher swing level results in better HP Low Clock Rate –41
phase noise performance but consumes High Clock Rate –100
more power. Medium Clock Rate –177
The BB PLL generates all baseband LP Low Clock Rate –158
and data port related clocks. Similar to
the ADC, both HP BB PLL and LP BB PLL RF PLL
options are provided. The HP BB PLL has Medium Power Consumption –44
a programmable frequency range of 7.2 Best Phase Noise Low Power Consumption –84
GHz to 8.8 GHz, while the LP BB PLL has a High Power Consumption –50
programmable range of 3.3 GHz to 5 GHz.
The HP BB PLL offers greater flexibility in Best Power Consumption Medium Power Consumption –80
generating clocks to support a wider range Low Power Consumption –108
of sample rates. When the signal sample BB PLL
rate is greater than 53.33 MHz, the HP
CLK PLL must be used. The LP BB PLL has a Medium Power Consumption –5
limitation in supporting certain sample rates HP Low Power Consumption –10
but consumes less power. High Power Consumption –45
The receive LPF attenuates out-of-band Medium Power Consumption –47
signals by supporting a variable bandwidth LP Low Power Consumption –49
from 5 MHz to 50 MHz. It also converts the
baseband signal current to voltage. It could be RX LPF
configured in transimpedance amplifier (TIA) Medium Power Consumption –26
mode as a first-order single-pole filter, or in bi- Second Order Low Power Consumption –40
quad (BIQ) mode as a second-order filter with High Power Consumption –77
two complex poles in the transfer function.
While the in-band performance of both First Order Medium Power Consumption –101
modes is similar, the second-order BIQ mode Low Power Consumption –116
achieves additional out-of-band attenuation TX LPF
compared with the first-order TIA mode.
Figure 4 compares the simulated frequency Medium Power Consumption –29
response at different f1dB configurations Low Power Consumption –47
between these two filters. The selection of
the second-order LPF consumes more power at their highest power consumption option. For an FDD 1T1R LTE 20 MHz profile, by configuring
than the first-order mode. In addition to that, the highest power consumption option when both transmit and receive channels are active, the
the in-band noise of the second-order LPF is total power consumption of the ADRV9001 is measured at about 1800 mW. Note: even with the
around 2.5 dB higher than the first-order LPF. same configurations, measurement results might vary depending on hardware and temperature.
For both first-order and second-order modes, Table 1 presents the amount of power saving achieved through configuring different power
the user can further select three different saving options. In this 1T1R LTE 20 MHz profile, both Receive Channel 1 and Transmit Channel 1
power consumption levels at high, medium, are enabled and the LO is configured at 900 MHz. Note: the numbers in each row of Table 1 show
or low by sacrificing the noise and linearity the relative amount of power saving in mW by only enabling this single power saving option.
performance. For example, using HP ADC with Medium Clock Rate saves about 72 mW compared against the
The transmit LPF is a second-order
Butterworth filter used to attenuate the
sampling images of the digital-to-analogue
converter (DAC). It also converts the current
from the DAC to a voltage and reconstructs
the analogue spectrum by low-pass
filtering the output. Similar to the receive
LPF, it provides three options of power
consumption levels at high, medium, or low
at a cost of linearity performance.
Usually, the best performance could be
achieved by configuring all the components Figure 4: First-order and second-order Rx LPF frequency response at different LPF f1dB configurations.
EngineerIT | April 2022 | 14