Page 18 - EngineerIT April 2022
P. 18
ICT COMMUNICATION
trigger the power-up and power-down.
The wake-up time is short—around 4.5 μs.
The channel power saving Mode 1 further
powers down the channel’s internal PLL.
When the PLL is powering up, recalibration is
mandatory, so the PLL wake-up time includes
PLL power-up time and PLL calibration time.
The ADRV9001 provides two PLL calibration
modes: normal mode and fast mode. The
fast mode does not guarantee a lock over
the entire temperature range as the normal
mode does, but it is more suitable when the
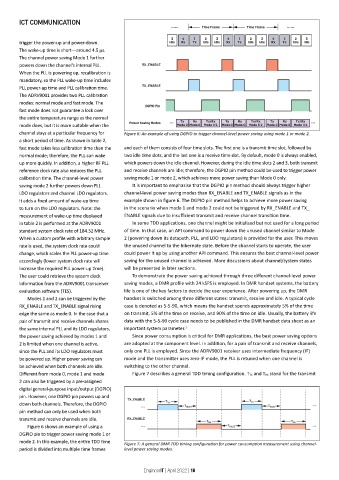
channel stays at a particular frequency for Figure 6: An example of using DGPIO to trigger channel-level power saving using mode 1 or mode 2.
a short period of time. As shown in table 2,
fast mode takes less calibration time than the and each of them consists of four time slots. The first one is a transmit time slot, followed by
normal mode; therefore, the PLL can wake two idle time slots, and the last one is a receive time slot. By default, mode 0 is always enabled,
up more quickly. In addition, a higher RF PLL which powers down the idle channel. However, during the idle time slots 2 and 3, both transmit
reference clock rate also reduces the PLL and receive channels are idle; therefore, the DGPIO pin method could be used to trigger power
calibration time. The channel-level power saving mode 1 or mode 2, which achieves more power saving than Mode 0 only.
saving mode 2 further powers down PLL It is important to emphasise that the DGPIO pin method should always trigger higher
LDO regulators and channel LDO regulators. channel-level power saving modes than RX_ENABLE and TX_ENABLE signals as in the
It adds a fixed amount of wake-up time example shown in figure 6. The DGPIO pin method helps to achieve more power saving
to turn on the LDO regulators. Note: the in the scenario when mode 1 and mode 2 could not be triggered by RX_ENABLE and TX_
measurement of wake-up time displayed ENABLE signals due to insufficient transmit and receive channel transition time.
in table 2 is performed at the ADRV9001 In some TDD applications, one channel might be initialised but not used for a long period
standard system clock rate of 184.32 MHz. of time. In that case, an API command to power down the unused channel similar to Mode
When a custom profile with arbitrary sample 2 (powering down its datapath, PLL, and LDO regulators) is provided for the user. This moves
rate is used, the system clock rate could the unused channel to the hibernate state. Before the channel starts to operate, the user
change, which scales the PLL power-up time could power it up by using another API command. This ensures the best channel-level power
accordingly (lower system clock rate will saving for the unused channel is achieved. More discussions about channel/system states
increase the required PLL power-up time). will be presented in later sections.
The user could retrieve the system clock To demonstrate the power saving achieved through three different channel-level power
information from the ADRV9001 transceiver saving modes, a DMR profile with 24 kSPS is employed. In DMR handset systems, the battery
evaluation software (TES). life is one of the key factors to decide the user experience. After powering up, the DMR
Modes 1 and 2 can be triggered by the handset is switched among three different states: transmit, receive and idle. A typical cycle
RX_ENABLE and TX_ENABLE signal rising case is denoted as 5-5-90, which means the handset spends approximately 5% of the time
edge the same as mode 0. In the case that a on transmit, 5% of the time on receive, and 90% of the time on idle. Usually, the battery life
pair of transmit and receive channels shares data with the 5-5-90 cycle case needs to be published in the DMR handset data sheet as an
the same internal PLL and its LDO regulators, important system parameter. 1
the power saving achieved by modes 1 and Since power consumption is critical for DMR applications, the best power saving options
2 is limited when one channel is active, are adopted at the component level. In addition, for a pair of transmit and receive channels,
since the PLL and its LDO regulators must only one PLL is employed. Since the ADRV9001 receiver uses intermediate frequency (IF)
be powered up. Higher power saving can mode and the transmitter uses zero-IF mode, the PLL is retuned when one channel is
be achieved when both channels are idle. switching to the other channel.
Different from mode 0, mode 1 and mode Figure 7 describes a general TDD timing configuration. T TX and T RX stand for the transmit
2 can also be triggered by a pre-assigned
digital general-purpose input/output (DGPIO)
pin. However, one DGPIO pin powers up and
down both channels. Therefore, the DGPIO
pin method can only be used when both
transmit and receive channels are idle.
Figure 6 shows an example of using a
DGPIO pin to trigger power saving mode 1 or
mode 2. In this example, the entire TDD time Figure 7: A general DMR TDD timing configuration for power consumption measurement using channel-
period is divided into multiple time frames level power saving modes.
EngineerIT | April 2022 | 16